Difference between revisions of "Pentachlorophenol"
(username removed) |
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
[http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0069.html International Chemical Safety Card] | [http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0069.html International Chemical Safety Card] | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, ''A Guide to Museum Pest Control'', FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988 | * Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, ''A Guide to Museum Pest Control'', FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988 | ||
Revision as of 14:45, 1 May 2016
Description
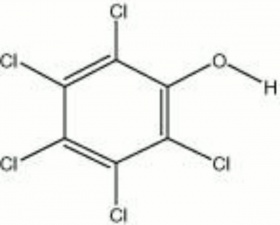
Colorless, crystalline powder that was made by the chlorination of phenol. Pentachlorophenol (PCP) was used as a fungicide, bactericide, and algicide. It was used commercially for the preservation of wood, paper, starch, dextrin, and glue. When tested as a potential fungicide in a closed container, PCP produced enough hydrogen chloride to corrode iron fasteners within 24 hours. The sodium salt, sodium pentachlorophenate or PCPNa (Santobrite and Dowicide G), is sometimes used as a replacement to minimize acid formation. Some objects (paper, textiles, leather, and historic wood buildings) may still contain toxic levels of PCP due to its wide use prior to 1987 when its use in the U.S. was banned.
Synonyms and Related Terms
PCP; Penta; penchlorol; pentachlorphenol; Santophen 20 [Monsanto]; Santobrite (PCPNa) [Monsanto]; Dowicide EC7 [Dow Chemical]; Dowicide G (PCPNa) [Dow Chemical]; Weedone
Other Properties
Needle-like crystals. Soluble in dilute alkali, ethanol, ether, benzene. Slightly soluble in water.
| Composition | C6Cl5OH |
|---|---|
| CAS | 87-86-5 |
| Melting Point | 190-191 |
| Density | 1.978 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt.=266.4 |
| Boiling Point | 309-310 |
Hazards and Safety
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. LD50 = 146=175 mg/kg
Can corrode metals. May discolor wood, textiles, and pigments.
Noncombustible.
International Chemical Safety Card
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, A Guide to Museum Pest Control, FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988
- G.Caneva, M.P.Nugari, O.Salvadori, Biology in the Conservation of Works of Art, ICCROM, Rome, 1991
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 7242
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 413
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pentachlorophenol (Accessed Feb. 10, 2006)