Difference between revisions of "Silver oxide"
(username removed) |
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
Mallinckrodt Baker: [http://www.jtbaker.com/msds/englishhtml/s2330.htm MSDS] | Mallinckrodt Baker: [http://www.jtbaker.com/msds/englishhtml/s2330.htm MSDS] | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* Marie Svoboda, Conservation Survey Index, unpublished, 1997 | * Marie Svoboda, Conservation Survey Index, unpublished, 1997 | ||
Revision as of 17:30, 1 May 2016
Description
Dark brown or black powder. Silver oxide is used for polishing glass and for coloring glass yellow. It has also been used at excavation sites for the treatment of bronze disease. However, it is not as effective as benzotriazole and can leave dark spots on the surface. Silver oxide is used medicinally as a germicide.
Synonyms and Related Terms
argentous oxide; argenticoxide; silver peroxide; disilver oxide
Other Properties
Soluble in solutions of ammonium hydroxide, potassium cyanide sodium thiosulfate and nitric acid. Slightly soluble in water. Insoluble in ethanol.
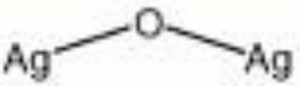
| Composition | Ag2O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 20667-12-3 |
| Melting Point | 300 (dec) |
| Density | 7.14-7.22 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 231.74 |
Hazards and Safety
Fire and explosion risk in contact with organic materials or ammonia. Decomposes in sunlight to form metallic silver and oxygen. Contact may cause iiritation and staining.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- Marie Svoboda, Conservation Survey Index, unpublished, 1997
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998