Difference between revisions of "Young fustic (Cotinus coggygria ) LC"
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:|thumb|''' | + | [[File:Smoke tree.jpg|thumb|''cotinus coggygria''. Photo by X. Zhang]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| + | A natural yellow dyestuff obtained from the wood of the smoketree, Cotinus coggygria (formerly Rhus cotinus). This small tree, also called Venetian sumac, is native to southern Europe, the Middle East, India and China. | ||
== Historical importance == | == Historical importance == | ||
| − | = Summary of results = | + | == Summary of results == |
| + | The primary coloring compounds are fisetin and sulferitin. Young fustic has poor lightfastness. | ||
| + | == Analytical instrumentation and procedures == | ||
| − | + | HPLC-DAD-MS analysis was performed with an Agilent 1100 liquid chromatography system consisting of an automatic injector, a gradient pump, a HP series 1100 DAD, and an Agilent series 1100 VL on-line atmospheric pressure ionization electrospray ionization mass spectrometer. Separations were done on a Vydac 214TP52 analytical column (2.1 mm diameterX250 mm; 5-ím particle size). The column was eluted at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min with a tertiary gradient of water (A),acetonitrile (B), and 1% (v/v) aqueous formic acid (C) with the following elution program: 0 min, 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; 0-55 min, a linear gradient to 35% A, 60% B, 5% C; 55-60 min, a linear gradient elution to 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 60-62 min, isocratic elution at 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 62-70 min gradient elution to 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; and reequilibration with the latter solvent for 15 min. The mass spectrometer was run both in the negative and positive ion mode. | |
| − | + | == Chromatograms == | |
| − | = Chromatograms = | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
[[File:Young fustic info.PNG|center|frame|sample information, By R. A. Laursen, Boston University ]] | [[File:Young fustic info.PNG|center|frame|sample information, By R. A. Laursen, Boston University ]] | ||
| − | = Identified compounds = | + | == Identified compounds == |
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|~HPLC-DAD|.JPG~ UV-Vis|.jpg~ UV-Vis]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|~HPLC-DAD|.JPG~ UV-Vis|.jpg~ UV-Vis]]] | ||
| Line 69: | Line 71: | ||
| − | [[Category:Analysis | + | [[Category:Dye Analysis]] |
| + | [[Category:Reference Materials]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Natural Dyes]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:24, 29 September 2017
Description
A natural yellow dyestuff obtained from the wood of the smoketree, Cotinus coggygria (formerly Rhus cotinus). This small tree, also called Venetian sumac, is native to southern Europe, the Middle East, India and China.
Historical importance
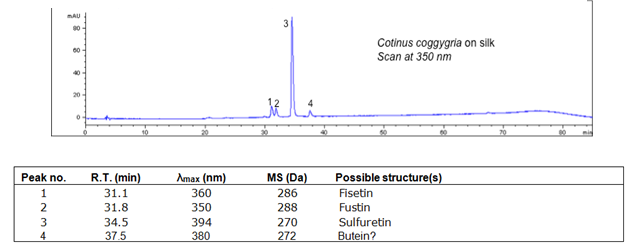
Summary of results
The primary coloring compounds are fisetin and sulferitin. Young fustic has poor lightfastness.
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
HPLC-DAD-MS analysis was performed with an Agilent 1100 liquid chromatography system consisting of an automatic injector, a gradient pump, a HP series 1100 DAD, and an Agilent series 1100 VL on-line atmospheric pressure ionization electrospray ionization mass spectrometer. Separations were done on a Vydac 214TP52 analytical column (2.1 mm diameterX250 mm; 5-ím particle size). The column was eluted at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min with a tertiary gradient of water (A),acetonitrile (B), and 1% (v/v) aqueous formic acid (C) with the following elution program: 0 min, 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; 0-55 min, a linear gradient to 35% A, 60% B, 5% C; 55-60 min, a linear gradient elution to 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 60-62 min, isocratic elution at 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 62-70 min gradient elution to 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; and reequilibration with the latter solvent for 15 min. The mass spectrometer was run both in the negative and positive ion mode.
Chromatograms
Sample information
Identified compounds
| Compound | RT (min.) | MW | UV/vis | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fisetin | 31.1 | 286 | 360 | Comments here |
| Fustin | 31.8 | 288 | 350 | |
| Sulfuretin | 34.5 | 270 | 394 | |
| Butein | 37.5 | 272 | 380 |
References
[1] [2] [3]