Difference between revisions of "Chinese grass (Miscanthus tinctorius) LC"
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| + | Chinese grass (''Miscanthus tinctorius'') is also called kariyasu, yama kariyasu (mountain kariyasu) or kizome gusa (graa for making yellow) in Japanese. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chinese grass is a tufted perennial grass with culms 80-100 cm long. | ||
== Historical importance == | == Historical importance == | ||
| − | = Summary of results = | + | == Summary of results == |
| − | = Analytical instrumentation and procedures = | + | == Analytical instrumentation and procedures == |
| + | HPLC-DAD-MS analysis was performed with an Agilent 1100 liquid chromatography system consisting of an automatic injector, a gradient pump, a HP series 1100 DAD, and an Agilent series 1100 VL on-line atmospheric pressure ionization electrospray ionization mass spectrometer. Separations were done on a Vydac 214TP52 analytical column (2.1 mm diameterX250 mm; 5-ím particle size). The column was eluted at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min with a tertiary gradient of water (A),acetonitrile (B), and 1% (v/v) aqueous formic acid (C) with the following elution program: 0 min, 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; 0-55 min, a linear gradient to 35% A, 60% B, 5% C; 55-60 min, a linear gradient elution to 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 60-62 min, isocratic elution at 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 62-70 min gradient elution to 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; and reequilibration with the latter solvent for 15 min. The mass spectrometer was run both in the negative and positive ion mode. | ||
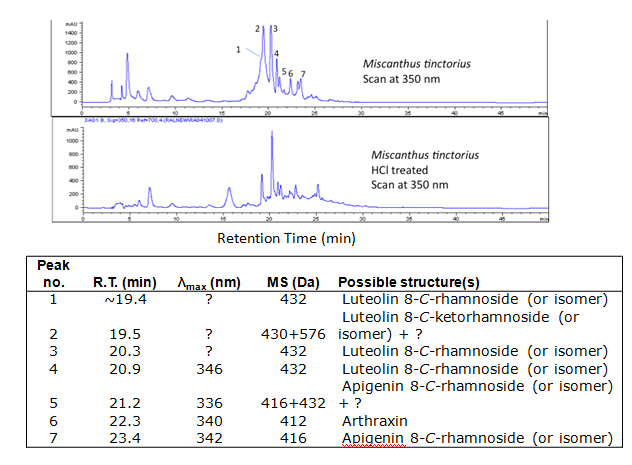
| − | = Chromatograms = | + | == Chromatograms == |
| Line 20: | Line 24: | ||
[[File:Chinese grass lc.PNG|center|frame|Absorbance at 350nm (mAU)]] | [[File:Chinese grass lc.PNG|center|frame|Absorbance at 350nm (mAU)]] | ||
| − | Sample information | + | == Sample information == |
[[File:Chinese grassinfo.PNG|center|frame|Sample information, by R. Laursen, Boston University]] | [[File:Chinese grassinfo.PNG|center|frame|Sample information, by R. Laursen, Boston University]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 69: | Line 38: | ||
[[Category:Dye Analysis]] | [[Category:Dye Analysis]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Reference Materials]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Natural Dyes]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:24, 22 March 2018
Description
Chinese grass (Miscanthus tinctorius) is also called kariyasu, yama kariyasu (mountain kariyasu) or kizome gusa (graa for making yellow) in Japanese.
Chinese grass is a tufted perennial grass with culms 80-100 cm long.
Historical importance
Summary of results
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
HPLC-DAD-MS analysis was performed with an Agilent 1100 liquid chromatography system consisting of an automatic injector, a gradient pump, a HP series 1100 DAD, and an Agilent series 1100 VL on-line atmospheric pressure ionization electrospray ionization mass spectrometer. Separations were done on a Vydac 214TP52 analytical column (2.1 mm diameterX250 mm; 5-ím particle size). The column was eluted at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min with a tertiary gradient of water (A),acetonitrile (B), and 1% (v/v) aqueous formic acid (C) with the following elution program: 0 min, 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; 0-55 min, a linear gradient to 35% A, 60% B, 5% C; 55-60 min, a linear gradient elution to 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 60-62 min, isocratic elution at 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 62-70 min gradient elution to 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; and reequilibration with the latter solvent for 15 min. The mass spectrometer was run both in the negative and positive ion mode.
Chromatograms
Sample information
References
[1] [2] [3]