Difference between revisions of "Krazy glue"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Krazy glue; crazy glue (sp); cyanoacrylate | Krazy glue; crazy glue (sp); cyanoacrylate | ||
| + | == Applications == | ||
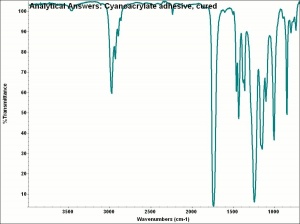
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiCYANOacrylate.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiCYANOacrylate.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| − | + | May cause irritation to skin and eyes. Will adhere objects on contact, including skin. | |
| − | + | Elmers: [http://www.elmers-glue.com/msds/MKG0824CN_A.HTM MSDS] | |
| − | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | |
| − | + | Uncured glue soluble in acetone and methanol. Cured glue is slightly soluble in DMF or nitromethane. Soaking in acetone may decrease adhesion and cause the join to separate. | |
== Sources Checked for Data in Record == | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == | ||
| − | * | + | * C.V.Horie, ''Materials for Conservation'', Butterworth-Heineman, London, 1997 |
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 |
| − | * | + | * Irving Skeist, ''Handbook of Adhesives'', Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 15:30, 19 May 2020
Description
[Borden] A registered trademark for a cyanoacrylate adhesive. Krazy Glue contains 99.95% ethyl cyanoacrylate and 0.05% acrylic. Cyanoacrylates are quickly polymerized by exposure to moisture and ultraviolet light. When cured, it forms an extremely strong bond that is fairly insoluble. Cyanoacrylate glues has been used for gluing glass, ceramics and other hard materials. They also have medical and dental applications to suture skin and weld crowns. Some cyanoacrylate glues may lose adhesive strength with time. Ultraviolet light and contact with alkaline materials (glass and some stones) will accelerate the degradation process.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Krazy glue; crazy glue (sp); cyanoacrylate
Applications
Risks
May cause irritation to skin and eyes. Will adhere objects on contact, including skin.
Elmers: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Uncured glue soluble in acetone and methanol. Cured glue is slightly soluble in DMF or nitromethane. Soaking in acetone may decrease adhesion and cause the join to separate.
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- C.V.Horie, Materials for Conservation, Butterworth-Heineman, London, 1997
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- Irving Skeist, Handbook of Adhesives, Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977