Difference between revisions of "Medulla"
(username removed) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
medullary cell | medullary cell | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | * | + | * Walter C. McCrone, John Gustave Delly, ''The Particle Atlas'', W. McCrone Associates, Chicago, IV, 1972 |
| − | * | + | * Edward Reich, Carlton J. Siegler, ''Consumer Goods: How to Know and Use Them'', American Book Company, New York City, 1937 |
| − | * | + | * F. Kidd, ''Brushmaking Materials'', Bristish Brush Manufacturers, London, 1957 |
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
Latest revision as of 12:36, 4 August 2020
Description
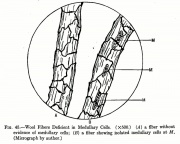
The inner core of a cellular structure. In plants, the medulla is composed of vertical bands of tissue between the pith and the bark. The fiber receives nourishment through the medulla. In animal hair, the medulla forms one to six parallel rows of air spaces in the central core. When the length of a hair or fiber is examined microscopically, the pattern of cells in the medulla is characterized as either continuous, intermediate or discontinuous depending on whether they are interconnecting or separate. Additionally a continuous medulla can be further subdivided as either nodose (irregular outline) or homogeneous (smooth outline). The medulla of some hairs, such as squirrel, are discontinuous at the tip, but continuous at the base.
Synonyms and Related Terms
medullary cell
Resources and Citations
- Walter C. McCrone, John Gustave Delly, The Particle Atlas, W. McCrone Associates, Chicago, IV, 1972
- Edward Reich, Carlton J. Siegler, Consumer Goods: How to Know and Use Them, American Book Company, New York City, 1937
- F. Kidd, Brushmaking Materials, Bristish Brush Manufacturers, London, 1957
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998