Difference between revisions of "Pitch pine"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:25.620-E10286CR-d1.jpg|thumb| | + | [[File:25.620-E10286CR-d1.jpg|thumb|Shumway House parlor<br>MFA#: 25.620]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
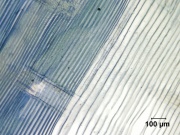
| − | + | [[File:54_Pitch Pine2_Rad2_100x.jpg|thumb|Pitch pine radial (''Pinus rigida'')]] | |
A medium size North American pine tree, ''Pinus rigida'', found generally in mid-Atlantic states. The pitch pine produced a sappy wood that made it excellent to make charcoal in Colonial America. It was occasionally used for ship building, mine timbers, railroad ties, briges and barns. Nowadays the tree is used mainly for rough construction, pulp, crating, and fuel. Pitch pine yields [[pitch|pitch]] and [[turpentine%20%28oil%29|turpentine]]. The wood's high resin content preserves it from decay. | A medium size North American pine tree, ''Pinus rigida'', found generally in mid-Atlantic states. The pitch pine produced a sappy wood that made it excellent to make charcoal in Colonial America. It was occasionally used for ship building, mine timbers, railroad ties, briges and barns. Nowadays the tree is used mainly for rough construction, pulp, crating, and fuel. Pitch pine yields [[pitch|pitch]] and [[turpentine%20%28oil%29|turpentine]]. The wood's high resin content preserves it from decay. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
''Pinus rigida''; pichepin (Fr.) | ''Pinus rigida''; pichepin (Fr.) | ||
| + | [[File:54_Pitch Pine2_Tan_100x.jpg|thumb|Pitch pine tangential (''Pinus rigida'')]] | ||
| + | [[File:54_Pitch Pine2_Tran_100x.jpg|thumb|Pitch pine transverse(''Pinus rigida'')]] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | + | * Evergreen needles: 2 1/2 to 5 inches (6-13 cm ) long | |
| − | + | * Cones: ovoid, 2 to 4 inches (5-10 cm) long, light brown in color | |
| − | + | * Bark: mature trees have brownish thick flat plates with deep furrows | |
| − | + | * Height: may reach 80 feet (25 m) | |
| − | + | * Density = 52-53 ppcf | |
| − | Evergreen needles: 2 1/2 to 5 inches (6-13 cm ) long | ||
| − | |||
| − | Cones: ovoid, 2 to 4 inches (5-10 cm) long, light brown in color | ||
| − | |||
| − | Bark: mature trees have brownish thick flat plates with deep furrows | ||
| − | |||
| − | Height: may reach 80 feet (25 m) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
Latest revision as of 10:44, 8 October 2020
Description
A medium size North American pine tree, Pinus rigida, found generally in mid-Atlantic states. The pitch pine produced a sappy wood that made it excellent to make charcoal in Colonial America. It was occasionally used for ship building, mine timbers, railroad ties, briges and barns. Nowadays the tree is used mainly for rough construction, pulp, crating, and fuel. Pitch pine yields Pitch and turpentine. The wood's high resin content preserves it from decay.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Pinus rigida; pichepin (Fr.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Evergreen needles: 2 1/2 to 5 inches (6-13 cm ) long
- Cones: ovoid, 2 to 4 inches (5-10 cm) long, light brown in color
- Bark: mature trees have brownish thick flat plates with deep furrows
- Height: may reach 80 feet (25 m)
- Density = 52-53 ppcf
Resources and Citations
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=52-53 ppcf (0.83-0.85 g/cm3)