Difference between revisions of "Ponderosa pine"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:17_PonderosaPine.jpg|thumb|Ponderosa Pine (''Pinus ponderosa'')]] | [[File:17_PonderosaPine.jpg|thumb|Ponderosa Pine (''Pinus ponderosa'')]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
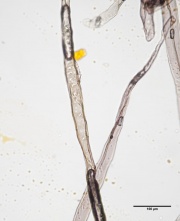
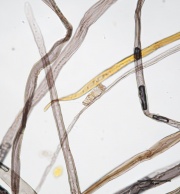
| + | [[File:Ponderosa pine 40x pinoid.jpg|thumb|Ponderosa pine paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain]] | ||
| + | A large pine tree, ''Pinus ponderosa'', native to the western U.S. and Canada. Ponderosa pine produces a white, fine-grain, soft wood that is used for the construction of furniture, millwork, flooring, houses, and ships. Native Americans used its long needles (up to 10') to weave baskets and jewelry. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[File:Ponderosa pine 40x.jpg|thumb|Ponderosa pine paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain]] | [[File:Ponderosa pine 40x.jpg|thumb|Ponderosa pine paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain]] | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
''Pinus ponderosa''; western yellow pine; bull pine; silver pine; yellow pine; heavy wooded pine; pin de Ponderosa (Fr.); pinho-de-Ponderosa (Port.) | ''Pinus ponderosa''; western yellow pine; bull pine; silver pine; yellow pine; heavy wooded pine; pin de Ponderosa (Fr.); pinho-de-Ponderosa (Port.) | ||
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | + | * Height: Large tree with heights to 72 m and circumference to 820 cm. | |
| − | Density = 25-28 pcf | + | * Bark: Browish-black on young trees changing to broad orange-red plates on mature trees. |
| + | * Leaves: Long needles (11 to 20 cm) in fassicles of two or three | ||
| + | * Density = 25-28 pcf | ||
Paper fiber type: softwood, hard pine. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified the presence of pinoid pits in irregular groups. Pits may coalesce into one larger pit. Early wood and late wood fibers are distinct. Dentate ray tracheids are present. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.6mm, width 35-45μm. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]] and [[sulfite process|sulfite]]. Can be difficult to distinguish from other hard pines. | Paper fiber type: softwood, hard pine. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified the presence of pinoid pits in irregular groups. Pits may coalesce into one larger pit. Early wood and late wood fibers are distinct. Dentate ray tracheids are present. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.6mm, width 35-45μm. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]] and [[sulfite process|sulfite]]. Can be difficult to distinguish from other hard pines. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 18: | ||
== Working Properties == | == Working Properties == | ||
Ponderosa pines produce a lightweight, hard, fine grained. strong wood. It has a reputation for being easy to work and was often chosen by carvers. The pine was also used for cabinets, furniture and toys. | Ponderosa pines produce a lightweight, hard, fine grained. strong wood. It has a reputation for being easy to work and was often chosen by carvers. The pine was also used for cabinets, furniture and toys. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Resources and Citations == | == Resources and Citations == | ||
Revision as of 11:00, 8 October 2020
Description
A large pine tree, Pinus ponderosa, native to the western U.S. and Canada. Ponderosa pine produces a white, fine-grain, soft wood that is used for the construction of furniture, millwork, flooring, houses, and ships. Native Americans used its long needles (up to 10') to weave baskets and jewelry.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Pinus ponderosa; western yellow pine; bull pine; silver pine; yellow pine; heavy wooded pine; pin de Ponderosa (Fr.); pinho-de-Ponderosa (Port.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Height: Large tree with heights to 72 m and circumference to 820 cm.
- Bark: Browish-black on young trees changing to broad orange-red plates on mature trees.
- Leaves: Long needles (11 to 20 cm) in fassicles of two or three
- Density = 25-28 pcf
Paper fiber type: softwood, hard pine. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified the presence of pinoid pits in irregular groups. Pits may coalesce into one larger pit. Early wood and late wood fibers are distinct. Dentate ray tracheids are present. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.6mm, width 35-45μm. Common pulping method: kraft and sulfite. Can be difficult to distinguish from other hard pines.
Working Properties
Ponderosa pines produce a lightweight, hard, fine grained. strong wood. It has a reputation for being easy to work and was often chosen by carvers. The pine was also used for cabinets, furniture and toys.
Resources and Citations
- Wood Magazine: https://www.woodmagazine.com/materials-guide/lumber/wood-species-3/ponderosa-pine (accessed (April 2020)
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 614
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- Western Pine Association, Portland, Oregon: air-dry weight = 28 pcf
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "pine." Accessed: 27 Oct. 2004 .
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.