Difference between revisions of "Yellow pine"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[File:Yellow pine MFA.jpg|thumb|Chest with drawers<br>MFA# 32.216]] | ||
| + | [[File:Fish on pin MFA.jpg|thumb|Fish on yellow pine<br>MFA# 48.485]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
In Southern US: [[longleaf pine]] (''Pinus palustris''), [[shortleaf pine]] (''Pinus echinata''); [[loblolly pine]] (''Pinus taeda''); southern yellow pine (common name) | In Southern US: [[longleaf pine]] (''Pinus palustris''), [[shortleaf pine]] (''Pinus echinata''); [[loblolly pine]] (''Pinus taeda''); southern yellow pine (common name) | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
File:SYP 40x pinoid.jpg|Southern yellow pine paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | File:SYP 40x pinoid.jpg|Southern yellow pine paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
* R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | ||
Latest revision as of 15:06, 8 October 2020
Description
A general name for several species of pine trees in the US that contain a similar type of strong wood. The tall yellow pines produces a dense, close-grain wood with a high resin content. It expands and contracts with moisture often causing coatings to crack, flake and peel. Yellow pine is used for lumber and millwork.
Synonyms and Related Terms
In Western US: Jeffrey pine (Pinus jeffreyi), Ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa)
In Southern US: Longleaf pine (Pinus palustris), Shortleaf pine (Pinus echinata); Loblolly pine (Pinus taeda); southern yellow pine (common name)
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Density | 23-37 ppcf |
|---|
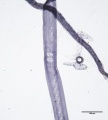
Paper fiber type: softwood, hard pine. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified by the presence of pinoid pits in horizontal groups. Southern yellow pines have more late wood fibers (with thicker walls) than early wood. Dentate ray tracheids are present. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 4mm, width 45μm. Common pulping method: kraft and sulfite. Very common paper fiber.
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 612
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Guy Weismantel, Paint Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 1981
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=23-37 ppcf (0.37-0.60 g/cm3)
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.