Difference between revisions of "Zinc yellow"
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Sissons Paints: [http://www.sissonspaints.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/MSDS-Q.D.-YELLOW-ZINC-CHROMATE-PRIMER.pdf MSDS] | Sissons Paints: [http://www.sissonspaints.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/MSDS-Q.D.-YELLOW-ZINC-CHROMATE-PRIMER.pdf MSDS] | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
Soluble in dilute acids including acetic acid. | Soluble in dilute acids including acetic acid. | ||
Revision as of 13:49, 27 October 2020
Description
A bright greenish yellow pigment derived by reacting Zinc oxide with Potassium dichromate solutions. The color shades of zinc yellow are variable depending on the proportions of each component. Vauquelin discovered the zinc yellow in 1809, but it was not developed as an artist colorant until 1847 by Murdock. Zinc yellow is toxic, stable to light, and unaffected by Hydrogen sulfide. However, it has less covering power than chrome yellow. The pure material has been used in oil and watercolors in recent years, but most zinc yellow is used in mixtures: a mixture with Prussian blue is sold as zinc chrome green and a mixture with Strontium yellow and Barium yellow is sold under the name Lemon yellow or Citron yellow. Zinc yellow is also used as a rust inhibitor and as a plastic colorant.
Synonyms and Related Terms
zinc chromate (VI) hydroxide; Pigment Yellow 36; CI 77955; Zinkgelb (Deut.); Zinkchromat (Deut.); jaune de zinc (Fr.); chromate de zinc (Fr.); chromate de jaune (Fr.); kitrino toy tsigkoy (Gr.); giallo di zinco (It.); giallo d'oro (It.); amarillo de cinc (Esp.); zinkchromaat (Ned.); amarelo de zinco (Port.); cromato de cinc (Esp.), cromato de zinco (Port.); zinc chromate yellow; zinc potassium chromate; buttercup yellow; primrose yellow; citron yellow; zinc chrome; permanent yellow; ultramarine yellow; yellow button of gold; lemon yellow
Risks
Human carcinogen. Skin contact may cause allergies. Acute ingestion may cause fatal chromium poisoning. Chronic inhalation may cause lung cancer and respiratory irritation.
May effloresce in humid conditions. May turn green with age.
Sissons Paints: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in dilute acids including acetic acid.
Insoluble in water (for modern synthetic zinc yellow); Some zinc yellows made in the 19th c. were slightly water soluble and were noted to effloresce in humid conditions (Doerner 1934).
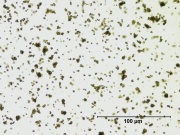
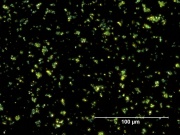
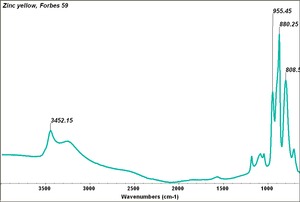
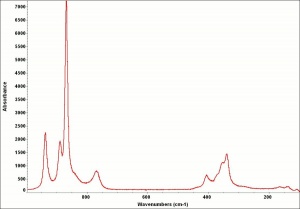
Appears microscopically as tiny round particles with a strong birefringence
| Composition | 4ZnO.4CrO3.K2O.3H2O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 37300-23-5 |
| Density | 3.4- 3.46 |
| Refractive Index | 1.84 - 1.9 |
Resources and Citations
- H. Kuhn, M.Curran, "Chrome Yellow and Other Chromate Pigments", Artists Pigments, Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986.
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: (density 3.46 and ref. index 1.84-1.9
- M. Doerner, The Materials of the Artist, Harcourt, Brace & Co., 1934
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 888
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- The Merck Index, Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 9933
- Colour Index International online at www.colour-index.org
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000