Difference between revisions of "Hollytex"
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
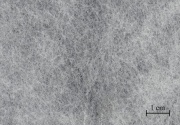
| − | [Ahlstrom Advanced Filtration] A registered trademark for a fabric series made with white, nonwoven fibers, with options available using either [[polyester fiber|polyester fibers]] or [[polyethylene fiber|polyethylene fibers]]. Hollytex® is spunbonded from continuous filaments resulting in a strong, lint-free, lightweight fabric with no added binders or pigments. It is calendared to produce a very smooth surface. Hollytex® is porous, but non-reactive, allowing moisture, vapors and liquids to pass through while effectively blocking particles. It is used as a support material, release paper, filtering agent, and interleaving paper. It is also used as a backing material for the 2-layer [[ | + | [Ahlstrom Advanced Filtration] A registered trademark for a fabric series made with white, nonwoven fibers, with options available using either [[polyester fiber|polyester fibers]] or [[polyethylene fiber|polyethylene fibers]]. Hollytex® is spunbonded from continuous filaments resulting in a strong, lint-free, lightweight fabric with no added binders or pigments. It is calendared to produce a very smooth surface. Hollytex® is porous, but non-reactive, allowing moisture, vapors and liquids to pass through while effectively blocking particles. It is used as a support material, release paper, filtering agent, and interleaving paper. It is also used as a backing material for the 2-layer [[Gore-Tex|GORE-TEX®]] laminate. |
[[File:Hollytex.jpg|thumb|Hollytex]] | [[File:Hollytex.jpg|thumb|Hollytex]] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
* Humidification, drying and flattening | * Humidification, drying and flattening | ||
* Barrier layer | * Barrier layer | ||
| + | == Personal Risks == | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Collection Risks == | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Environmental Risks == | ||
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| Line 26: | Line 31: | ||
! Grade || || Basis Weight (g/m3) || Thickness (mm) || Air Permeability (L/mm2/sec) || Material | ! Grade || || Basis Weight (g/m3) || Thickness (mm) || Air Permeability (L/mm2/sec) || Material | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #3220 || || | + | | #3220 || || 16.5 || 0.061 || 7040 || Polyester |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #3252 || || | + | | #3252 || || 30.5 || 0.058 || 1840 || Polyester |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #3254 || || | + | | #3254 || || 61.1 || 0.102 || 352 || Polyester |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #3256 || ||23.9 || 0.058 || 3640 || Polyester | + | | #3256 || || 23.9 || 0.058 || 3640 || Polyester |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #3257 || 32.3 || 0.074 || 2200 || Polyester | + | | #3257 || || 32.3 || 0.074 || 2200 || Polyester |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #3265 || 81.1 || 0.135 || 160 || Polyester | + | | #3265 || || 81.1 || 0.135 || 160 || Polyester |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #3271 || | + | | #3271 || || 111.6 || 0.211 || 264 || Polyester |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #3324 || 66.7 || 0.135 || 72 || Polyester | + | | #3324 || || 66.7 || 0.135 || 72 || Polyester |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #3329 || 96.5 || 0.135 || 41 || Polyester | + | | #3329 || || 96.5 || 0.135 || 41 || Polyester |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #6101 || 55.8 || 0.127 || 624 || Polyethylene | + | | #6101 || || 55.8 || 0.127 || 624 || Polyethylene |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #6102 || 201.5 || 0.368 || 40 || Polyethylene | + | | #6102 || || 201.5 || 0.368 || 40 || Polyethylene |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #6103 || 54.1 || 0.140 || 1200 || Polyethylene | + | | #6103 || || 54.1 || 0.140 || 1200 || Polyethylene |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | #6107 || 55.8 || 0.165 || 2800 || Polyethylene | + | | #6107 || || 55.8 || 0.165 || 2800 || Polyethylene |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 57: | Line 62: | ||
[[media:download_file_80.pdf|Properties of Synthetic Fibers]] | [[media:download_file_80.pdf|Properties of Synthetic Fibers]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
* Rachael Perkins Arenstein, Lisa Goldberg, and Eugenie Milroy, ‘Support and Rehousing for Collection Storage’ In ‘Preventive Conservation: Collection Storage’ Lisa Elkin and Christopher A. Norris (eds.), Society for the Preservation of Natural History Collections, New York. 2019. | * Rachael Perkins Arenstein, Lisa Goldberg, and Eugenie Milroy, ‘Support and Rehousing for Collection Storage’ In ‘Preventive Conservation: Collection Storage’ Lisa Elkin and Christopher A. Norris (eds.), Society for the Preservation of Natural History Collections, New York. 2019. | ||
| Line 73: | Line 78: | ||
| − | [[Category:Materials database]] [[Category:MWG]] [[Category:PACCIN]] | + | [[Category:Materials database]] [[Category:MWG]] [[Category:PACCIN]][[Category:Sheet, Fabric]][[Category: Interleaving]] |
Latest revision as of 14:41, 1 December 2020
Description
[Ahlstrom Advanced Filtration] A registered trademark for a fabric series made with white, nonwoven fibers, with options available using either polyester fibers or polyethylene fibers. Hollytex® is spunbonded from continuous filaments resulting in a strong, lint-free, lightweight fabric with no added binders or pigments. It is calendared to produce a very smooth surface. Hollytex® is porous, but non-reactive, allowing moisture, vapors and liquids to pass through while effectively blocking particles. It is used as a support material, release paper, filtering agent, and interleaving paper. It is also used as a backing material for the 2-layer GORE-TEX® laminate.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Holytex; Holly-Tex
Applications
- Lining, interleaving and as a release paper
- Support and backing
- Humidification, drying and flattening
- Barrier layer
Personal Risks
Collection Risks
Environmental Risks
Physical and Chemical Properties
Hollytex® has high tensile strength and high tear strength. Acid-free and non hygroscopic. Can be thermally and ultrasonically welded. Polyester is resistant to acids, oxidizing agents, solvents, rot and mildew. Dimensionally stable in all directions.
Forms/Sizes
Hollytex is sold in 60" wide rolls. Table shows available, weight, thicknesses, permeability and polymer type.
| Grade | Basis Weight (g/m3) | Thickness (mm) | Air Permeability (L/mm2/sec) | Material | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #3220 | 16.5 | 0.061 | 7040 | Polyester | |
| #3252 | 30.5 | 0.058 | 1840 | Polyester | |
| #3254 | 61.1 | 0.102 | 352 | Polyester | |
| #3256 | 23.9 | 0.058 | 3640 | Polyester | |
| #3257 | 32.3 | 0.074 | 2200 | Polyester | |
| #3265 | 81.1 | 0.135 | 160 | Polyester | |
| #3271 | 111.6 | 0.211 | 264 | Polyester | |
| #3324 | 66.7 | 0.135 | 72 | Polyester | |
| #3329 | 96.5 | 0.135 | 41 | Polyester | |
| #6101 | 55.8 | 0.127 | 624 | Polyethylene | |
| #6102 | 201.5 | 0.368 | 40 | Polyethylene | |
| #6103 | 54.1 | 0.140 | 1200 | Polyethylene | |
| #6107 | 55.8 | 0.165 | 2800 | Polyethylene |
Comparisons
Properties of Synthetic Fibers
Resources and Citations
- Rachael Perkins Arenstein, Lisa Goldberg, and Eugenie Milroy, ‘Support and Rehousing for Collection Storage’ In ‘Preventive Conservation: Collection Storage’ Lisa Elkin and Christopher A. Norris (eds.), Society for the Preservation of Natural History Collections, New York. 2019.
- AIC Wiki: Collaborative Knowledge Resource: http://www.conservation-wiki.com/w/index.php?title=Special%3ASearch&search=Hollytex&go=Go
- Conservation Support Systems (Hollytex): http://www.conservationsupportsystems.com/product/show/hollytex/lining-fabrics
- NEDCC (Holly-Tex): http://www.nedcc.org/plam3/tleaf64.htm
- Conservation by design (Holytex): http://www.conservation-by-design.co.uk/papers/papers28.html
- PEL (Holytex): http://www.preservationequipment.com/372.html
- Marie Svoboda, Conservation Survey Index, unpublished, 1997