Difference between revisions of "Acrilan"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:69 Acrilan16 200X pol.jpg|thumb|Acrilan®]] | [[File:69 Acrilan16 200X pol.jpg|thumb|Acrilan®]] | ||
| + | [[File:69 Acrilan16 200X.jpg|thumb|Acrilan®]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | [Solutia, Inc.] A registered trademark for an acrylonitrile-vinyl acetate copolymer fiber that is commonly used in textiles. Acrilan® was first produced in 1949 by Chemstrand Corp. After slight changes in the formulation and manufacturing procedures, Acrilan® was commercially manufactured in 1954. It is an [[acrylic%20fiber|acrylic fiber]] copolymerized with less than 15% vinyl acetate groups. Acrilans are noted for softness, strength and wrinkle-resistant properties. Acrilan® is used for clothing, carpets, drapes, upholstery and laminates. | + | [Solutia, Inc. (formerly Monsanto)] A registered trademark for an acrylonitrile-vinyl acetate copolymer fiber that is commonly used in textiles. Acrilan® was first produced in 1949 by Chemstrand Corp. After slight changes in the formulation and manufacturing procedures, Acrilan® was first commercially manufactured in 1954. It is an [[acrylic%20fiber|acrylic fiber]] copolymerized with less than 15% vinyl acetate groups. Acrilans are noted for softness, strength and wrinkle-resistant properties. Acrilan® is used for clothing, carpets, drapes, upholstery and laminates. Its wear resistance is better than that of wool, but generally greatly inferior to that of nylon or Terylene. It is unaffected by mildew, molds, moth and carpet beetle larvae. |
| − | + | In 2003, Solutia went into bankruptcy and reorganized. The Acrilan production plant closed in 2020. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
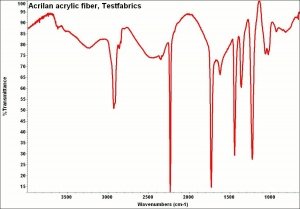
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|AcrilanTestfabrics.jpg~FTIR|acrilan300m.jpg~SEM]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|AcrilanTestfabrics.jpg~FTIR|acrilan300m.jpg~SEM]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, ethylene carbonate, and nitriles. | |
| − | + | * Insoluble in ethanol, acetone, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, and ligroin. | |
| − | + | * Density = 1.17 g/ml | |
| − | + | * Decomposes before it melts. Sticky at 245 C. | |
| − | + | * Prolonged exposure to air and heat causes yellowing | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 30: | Line 21: | ||
[[media:download_file_46.pdf|Properties of Synthetic Fibers]] | [[media:download_file_46.pdf|Properties of Synthetic Fibers]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| + | |||
| + | * Solutia: [http://www.acrilan.com/pages/index.html Acrilan® fiber] | ||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 | ||
| Line 40: | Line 33: | ||
* Meredith Montague, contributed information, 1998 | * Meredith Montague, contributed information, 1998 | ||
| − | * | + | * Solutia Inc. (formerly Monsanto Fibers) Website: [http://www.thesmartyarns.com/ Link] |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:19, 24 April 2022
Description
[Solutia, Inc. (formerly Monsanto)] A registered trademark for an acrylonitrile-vinyl acetate copolymer fiber that is commonly used in textiles. Acrilan® was first produced in 1949 by Chemstrand Corp. After slight changes in the formulation and manufacturing procedures, Acrilan® was first commercially manufactured in 1954. It is an Acrylic fiber copolymerized with less than 15% vinyl acetate groups. Acrilans are noted for softness, strength and wrinkle-resistant properties. Acrilan® is used for clothing, carpets, drapes, upholstery and laminates. Its wear resistance is better than that of wool, but generally greatly inferior to that of nylon or Terylene. It is unaffected by mildew, molds, moth and carpet beetle larvae.
In 2003, Solutia went into bankruptcy and reorganized. The Acrilan production plant closed in 2020.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, ethylene carbonate, and nitriles.
- Insoluble in ethanol, acetone, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, and ligroin.
- Density = 1.17 g/ml
- Decomposes before it melts. Sticky at 245 C.
- Prolonged exposure to air and heat causes yellowing
Comparisons
Properties of Synthetic Fibers
Resources and Citations
- Solutia: Acrilan® fiber
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- Fairchild's Dictionary of Textiles, Phyllis G.Tortora, Robert S. Merkel (eds.), Fairchild Publications, New York City, 7th edition, 1996
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Meredith Montague, contributed information, 1998
- Solutia Inc. (formerly Monsanto Fibers) Website: Link