Difference between revisions of "Anion exchange agent"
(username removed) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
anion exchange resin | anion exchange resin | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
Latest revision as of 12:27, 27 April 2022
Description
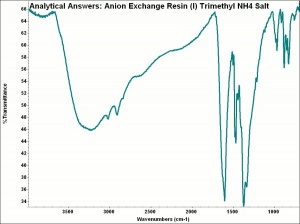
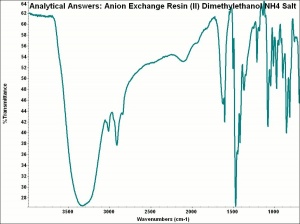
Any of several synthetic ion exchange resins that are designed to capture larger anions and release hydroxyl groups. Anion exchange resins usually contain a quaternary ammonium, secondary amine or tertiary amine active group. For water-softeners, anion exchange resins can substitute chloride ions for other less soluble anions such as hydroxyls, carbonates, and sulfates. In water-purifying systems, anion exchange resins are used second in line after a cation exchange resin. The first column removes the cations and replaces them with hydrogen ions to form acids. The anion exchange column removes the anions and substitutes hydroxyl ions to form water. Anion exchange resins are also used to purify organic compounds.
Synonyms and Related Terms
anion exchange resin
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 862