Blue verditer: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:blueverditer C100x.jpg|thumb|Blue verditer]] | [[File:blueverditer C100x.jpg|thumb|Blue verditer]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[File:44_Blue verditer_200X.jpg|thumb|Blue verditer]] | |||
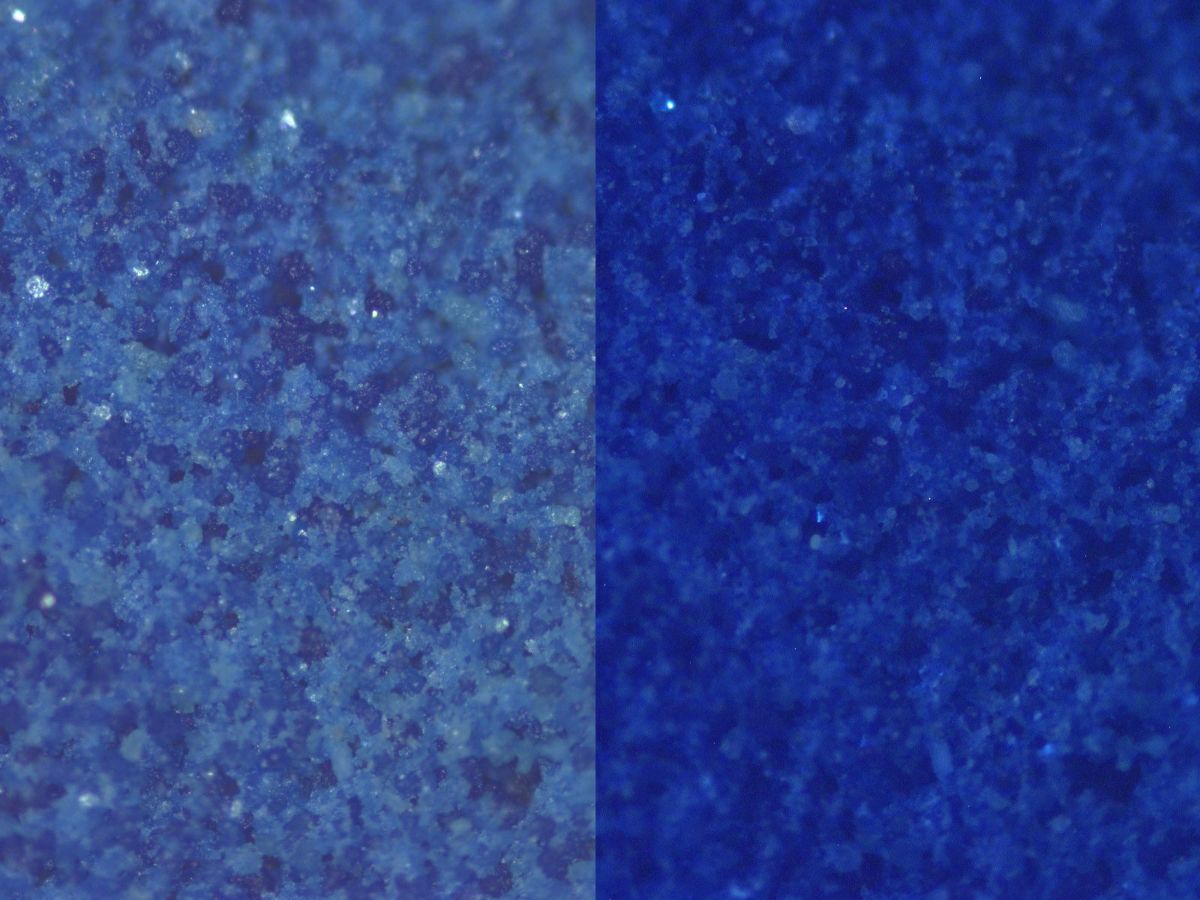
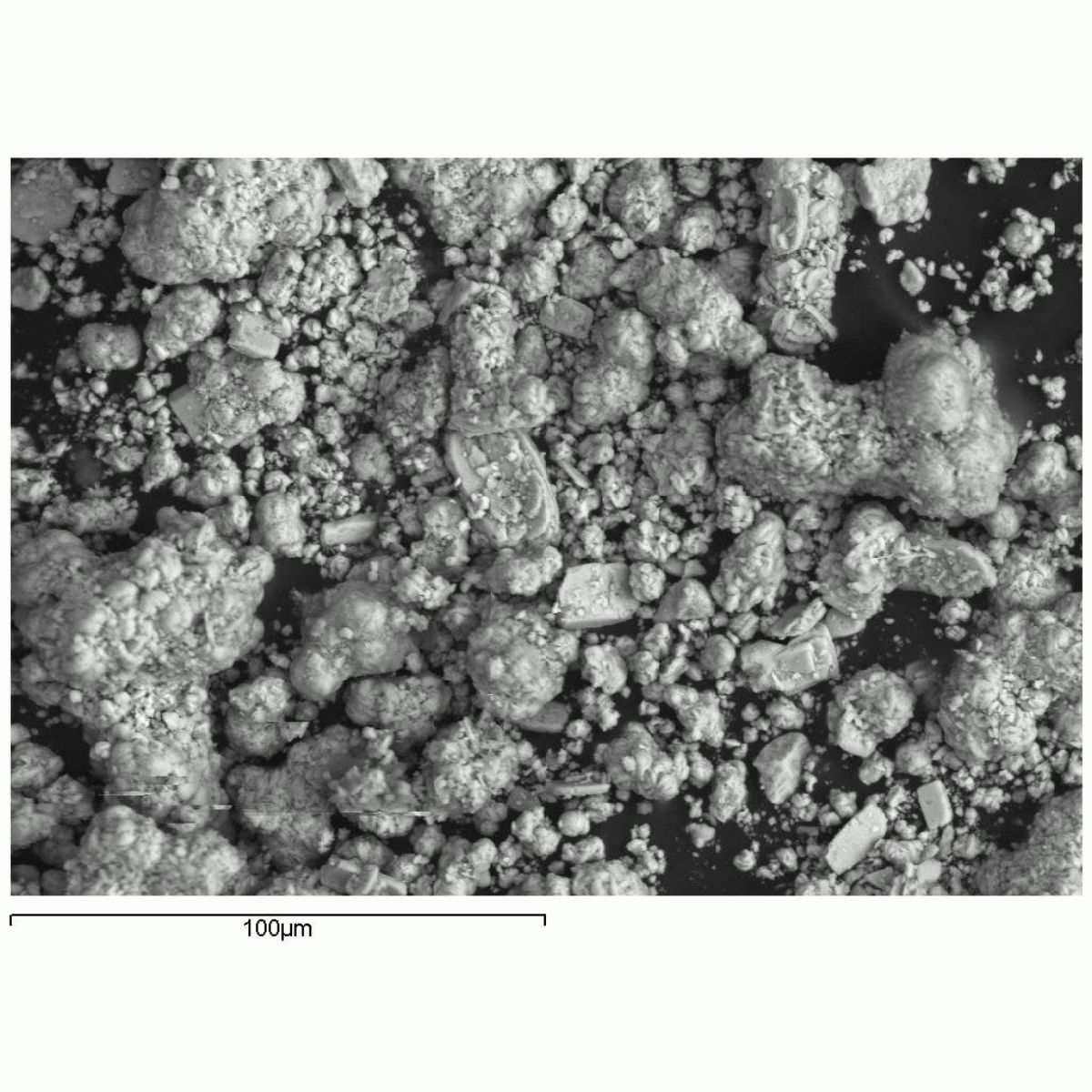
Synthetically prepared azure blue pigment composed of [[basic copper carbonate]]. Blue verditer was first made in the 17th century and became widely used in the 19th century for both [[distemper]] and [[oil paint|oil]] based interior house paints. It is no longer commonly used. Blue verditer particles are more rounded and regular in size than ground [[azurite]]. | Synthetically prepared azure blue pigment composed of [[basic copper carbonate]]. Blue verditer was first made in the 17th century and became widely used in the 19th century for both [[distemper]] and [[oil paint|oil]] based interior house paints. It is no longer commonly used. Blue verditer particles are more rounded and regular in size than ground [[azurite]]. | ||
[[File:44_Blue verditer_200X_pol.jpg|thumb|Blue verditer]] | [[File:44_Blue verditer_200X_pol.jpg|thumb|Blue verditer]] | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 11: | ||
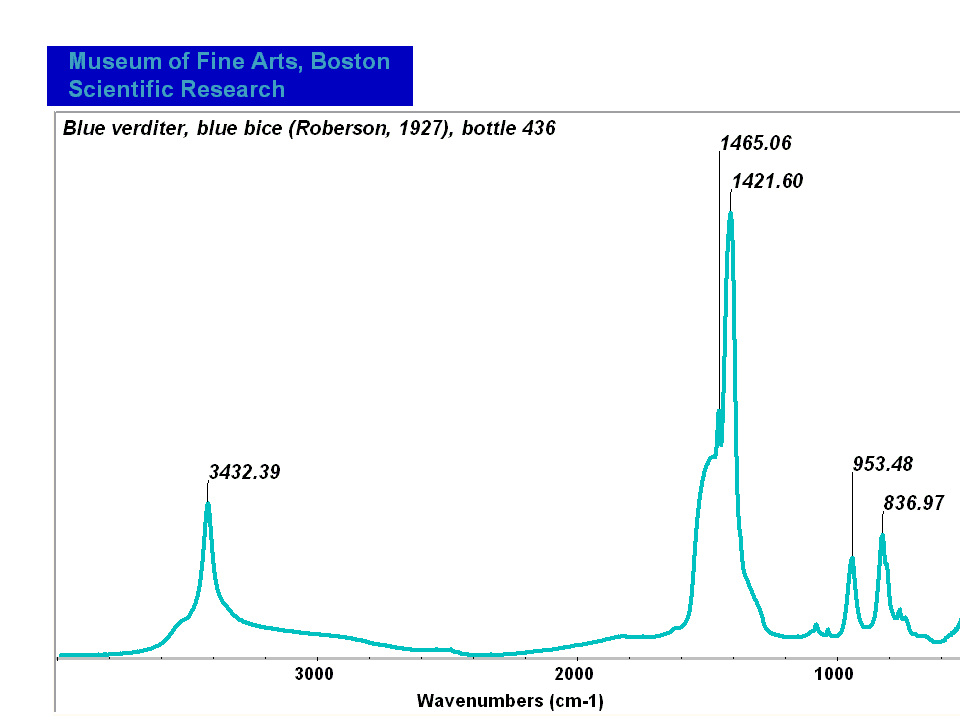
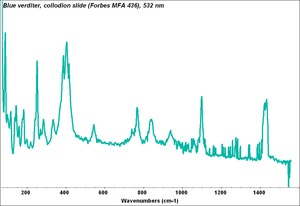
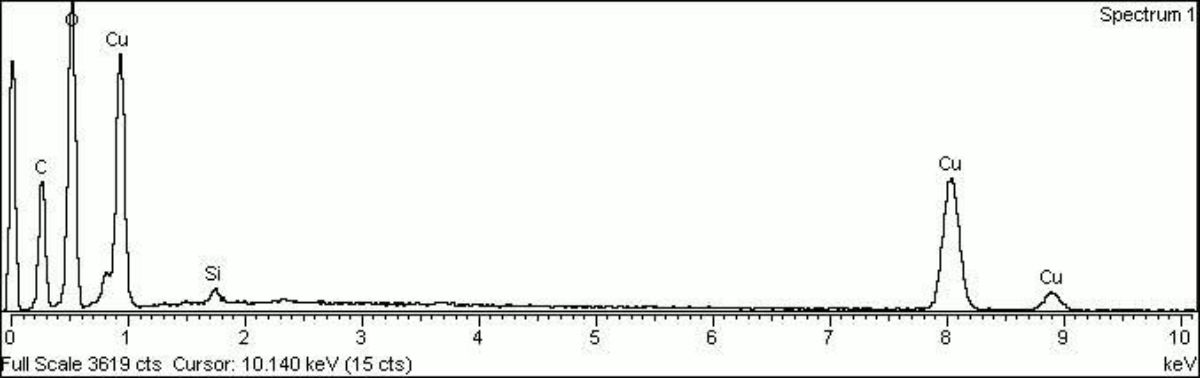
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Blue verditer (MFA 436).PNG~FTIR (MFA)|Blue verditer, collodion slide (Forbes MFA 436), 532 nm.TIF~Raman (MFA)| PIG436.jpg~XRD|f436sem.jpg~SEM|f436edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide3 F436.PNG~XRF]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Blue verditer (MFA 436).PNG~FTIR (MFA)|Blue verditer, collodion slide (Forbes MFA 436), 532 nm.TIF~Raman (MFA)| PIG436.jpg~XRD|f436sem.jpg~SEM|f436edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide3 F436.PNG~XRF]]] | ||
== | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
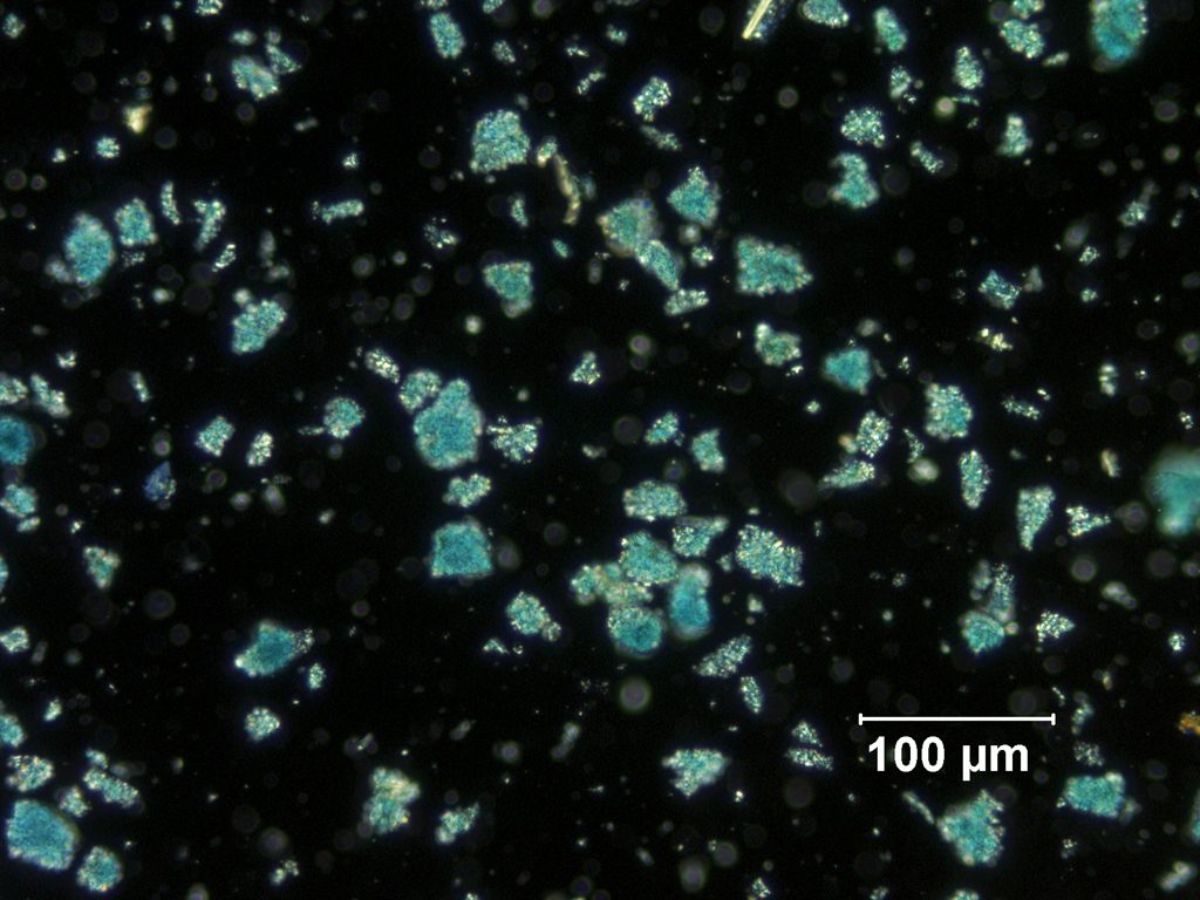
Microscopically appears as tiny round aggregates that are highly birefringent and blue in transmitted light. Pleochroic from pale blue to deep blue. | * Insoluble in water and ethanol. | ||
* Decomposes in acids with the evolution of carbon dioxide bubbles. | |||
* Turns black with warm alkalis, hydrogen sulfide or sulfur fumes. | |||
* Microscopically appears as tiny round aggregates that are highly birefringent and blue in transmitted light. | |||
* Pleochroic from pale blue to deep blue. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| 3.8 | | 3.8 g/ml | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
Latest revision as of 16:46, 8 May 2022
Description
Synthetically prepared azure blue pigment composed of basic copper carbonate. Blue verditer was first made in the 17th century and became widely used in the 19th century for both distemper and oil based interior house paints. It is no longer commonly used. Blue verditer particles are more rounded and regular in size than ground azurite.
Synonyms and Related Terms
basic copper carbonate (synthetic); Pigment Blue 30; CI 77420; Bremerblau (Deut.); bleu de Brême (Fr.); bleu de montagne (Fr.); azul montaña (Esp.); verdeterra blu (It.); basisch kopercarbonaat (syn) (Ned.); blue bice; copper blue; Bremen blue; cendres blue; ashes blue; mountain blue, lime blue
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Insoluble in water and ethanol.
- Decomposes in acids with the evolution of carbon dioxide bubbles.
- Turns black with warm alkalis, hydrogen sulfide or sulfur fumes.
- Microscopically appears as tiny round aggregates that are highly birefringent and blue in transmitted light.
- Pleochroic from pale blue to deep blue.
| Composition | 2CuCO3-Cu(OH)2 |
|---|---|
| Density | 3.8 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.730; 1.838; 1.758 |
Comparisons
Characteristics of Common Blue Pigments
Resources and Citations
- Artists' Pigments: A Handbook of their History and Characteristics, Ashok Roy (ed.), National Gallery of Art, Washington DC, Vol. 2, 1993 Comment: R. Gettens, and E. West Fitzhugh, "Azurite and Blue Verditer" cites uses of verditer in house paints as early as 1638 and 1671.
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) Comment: probably originating in the 18th c.; widely used in the 19th c.
- R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982 Comment: relatively new color in the 17th c.
- Kurt Wehlte, The Materials and Techniques of Painting, Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York, 1975
- R. Newman, E. Farrell, 'House Paint Pigments', Paint in America , R. Moss ed., Preservation Press, New York City, 1994
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000