Difference between revisions of "Butyl lactate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
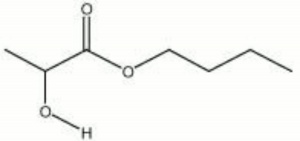
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|butyl lactate.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
| − | A colorless, stable, low volatility liquid. Butyl lactate is used as a solvent for [ | + | A colorless, stable, low volatility liquid. Butyl lactate is used as a solvent for [[paint|paints]], [[Lacquer, synthetic|lacquers]], [[varnish|varnishes]], [[oil|oils]], [[dye|dyes]], [[ink|inks]], and [[synthetic resin|synthetic resins]]. It is usually blended with other solvents to slow evaporation and increase drying times. Butyl lactate has also been used as a solvent for [[polyvinyl acetate]] based paints. Toch used small amounts of butyl lactate mixed with [[turpentine%20%28oil%29|turpentine]] for cleaning paintings (Toch 1931). |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
n-butyl lactate | n-butyl lactate | ||
| − | + | == Risks == | |
| − | == | + | * Combustible liquid and vapor. |
| + | * Flash point = 71 C. | ||
| + | * Toxic. | ||
| + | * Contact causes irritation | ||
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/96093.htm MSDS] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Miscible with most oils and organic solvents. Slightly soluble in water. Hydrolyzed with acids or alkalis. | Miscible with most oils and organic solvents. Slightly soluble in water. Hydrolyzed with acids or alkalis. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 27: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | -43 | + | | -43 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 0.974-0.984 | + | | 0.974-0.984 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 34: | Line 39: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ||
| − | | 188 | + | | 188 C |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * M. Toch, ''Paint, Paintings and Restoration'', D.Van Nostrand, New York, 1931. | |
| − | * | + | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 |
| − | * | + | * R. Mayer, ''The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques'', Viking Press, New York, 1981 |
| − | * | + | * Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) |
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:42, 11 May 2022
Description
A colorless, stable, low volatility liquid. Butyl lactate is used as a solvent for paints, lacquers, varnishes, oils, dyes, inks, and synthetic resins. It is usually blended with other solvents to slow evaporation and increase drying times. Butyl lactate has also been used as a solvent for Polyvinyl acetate based paints. Toch used small amounts of butyl lactate mixed with turpentine for cleaning paintings (Toch 1931).
Synonyms and Related Terms
n-butyl lactate
Risks
- Combustible liquid and vapor.
- Flash point = 71 C.
- Toxic.
- Contact causes irritation
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Miscible with most oils and organic solvents. Slightly soluble in water. Hydrolyzed with acids or alkalis.
| Composition | CH3CHOHCOOC4H9 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 138-22-7 |
| Melting Point | -43 C |
| Density | 0.974-0.984 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 146.19 |
| Refractive Index | 1.4216 |
| Boiling Point | 188 C |
Resources and Citations
- M. Toch, Paint, Paintings and Restoration, D.Van Nostrand, New York, 1931.
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- R. Mayer, The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques, Viking Press, New York, 1981
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993