Difference between revisions of "Cadmium red"
(username removed) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:181 cadmium red.jpg|thumb|Cadmium red]] | [[File:181 cadmium red.jpg|thumb|Cadmium red]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| + | [[File:cdred C100x.jpg|thumb|cadmium red at 100x; normal and UV light]] | ||
| + | A permanent, deep red pigment composed of cadmium sulfoselenide. Pure cadmium sulfoselenide was patented in Germany in 1892 and first sold as a pigment (C.P.) in artist paints in 1907. Variations in the proportions of the cadmium and selenide produce as range of colors from orange to dark maroon. In 1926, cadmium reds were co-precipitated with [[barium sulfate]] to form less expensive [[cadmopone|cadmium lithopone]] pigments. | ||
| − | + | See also [[cadmium sulfide]]. | |
| − | + | [[File:26_Cadmium_red_200X.jpg|thumb|Cadmium red]] | |
| − | See also [ | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[File: | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | cadmium sulfide; cadmium sulfoselenide; Pigment Red 108; CI 77196; rouge de cadmium (Fr.); Kadmiumrot (Deut.); rojo de cadmio (Esp.); kokkino toy kadmioy (Gr.); rosso cadmio (It.); cadmiumrood (Ned.); vermelho de | + | cadmium sulfide; cadmium sulfoselenide; Pigment Red 108; CI 77196; rouge de cadmium (Fr.); Kadmiumrot (Deut.); rojo de cadmio (Esp.); kokkino toy kadmioy (Gr.); rosso cadmio (It.); cadmiumrood (Ned.); vermelho de cádmio (Port.) |
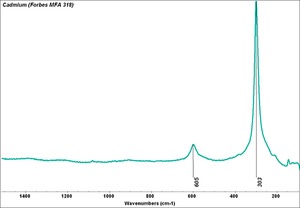
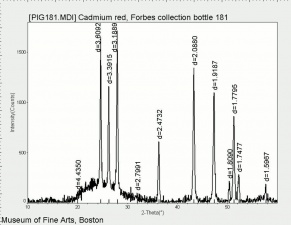
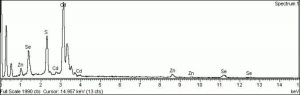
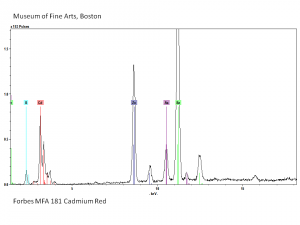
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign| | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Cadmium (Forbes MFA 318) resize.tif~Raman (MFA)|PIG181.jpg~XRD|f181sem.jpg~SEM|f191edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide15 FC181.PNG~XRF]]] |
| + | == Risks == | ||
| − | == | + | * Toxic by inhalation and ingestion. |
| + | * Carcinogen. | ||
| + | * May react with copper compounds and turn black. | ||
| + | * Gamblin Colors: [https://gamblincolors.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/SDSDryPigmentCadmiumRedYellowMedium.pdf SDS] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
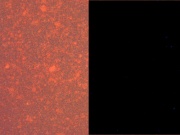
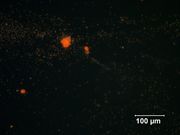
Tiny red particles less than 1 micrometer in diameter; deep red in transmitted light | Tiny red particles less than 1 micrometer in diameter; deep red in transmitted light | ||
| Line 23: | Line 27: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | + | * I. Fiedler, M. Bayard, "Cadmium yellows, oranges and reds", ''Artists Pigments'', Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | I. Fiedler, M. Bayard, "Cadmium yellows, oranges and reds", ''Artists Pigments'', Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | + | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 |
| − | * | + | * M. Doerner, ''The Materials of the Artist'', Harcourt, Brace & Co., 1934 |
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 |
| − | * | + | * Michael McCann, ''Artist Beware'', Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979 |
| − | * | + | * Monona Rossol, ''The Artist's Complete Health and Safety Guide'', Allworth Press, New York, 1994 |
| − | * | + | * Thomas B. Brill, ''Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities'', Plenum Press, New York City, 1980 |
* ''The Dictionary of Art'', Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: 'Pigments' | * ''The Dictionary of Art'', Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: 'Pigments' | ||
Latest revision as of 13:50, 11 May 2022
Description
A permanent, deep red pigment composed of cadmium sulfoselenide. Pure cadmium sulfoselenide was patented in Germany in 1892 and first sold as a pigment (C.P.) in artist paints in 1907. Variations in the proportions of the cadmium and selenide produce as range of colors from orange to dark maroon. In 1926, cadmium reds were co-precipitated with Barium sulfate to form less expensive cadmium lithopone pigments.
See also Cadmium sulfide.
Synonyms and Related Terms
cadmium sulfide; cadmium sulfoselenide; Pigment Red 108; CI 77196; rouge de cadmium (Fr.); Kadmiumrot (Deut.); rojo de cadmio (Esp.); kokkino toy kadmioy (Gr.); rosso cadmio (It.); cadmiumrood (Ned.); vermelho de cádmio (Port.)
Risks
- Toxic by inhalation and ingestion.
- Carcinogen.
- May react with copper compounds and turn black.
- Gamblin Colors: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Tiny red particles less than 1 micrometer in diameter; deep red in transmitted light
| Composition | CdS, CdSe |
|---|
Resources and Citations
- I. Fiedler, M. Bayard, "Cadmium yellows, oranges and reds", Artists Pigments, Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986.
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- M. Doerner, The Materials of the Artist, Harcourt, Brace & Co., 1934
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Monona Rossol, The Artist's Complete Health and Safety Guide, Allworth Press, New York, 1994
- Thomas B. Brill, Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities, Plenum Press, New York City, 1980
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: 'Pigments'
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000