Difference between revisions of "Calcium hydroxyapatite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 1670 | + | | 1670 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 3.18 | + | | 3.18 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
Revision as of 13:12, 18 May 2022
Description
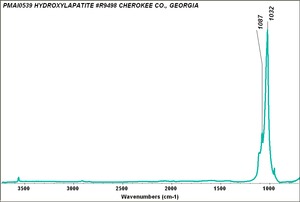
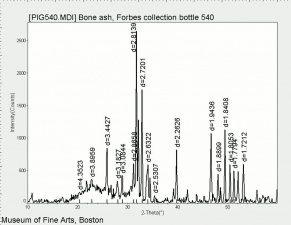
A white, odorless, tasteless powder. Bone is primarily composed of calcium hydroxyapatite mixed with Calcium carbonate and organic binders. Calcium hydroxyapatite is used in the manufacture of Milk glass, as a polishing powder, as a mordant and as a buffer.
See also Apatite.
Synonyms and Related Terms
tribasic calcium phosphate; tricalcium orthophosphate; tricalcium phosphate; bone ash
Risks
- Nonflammable.
- Merz USA: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in mineral acids. Insoluble in water, ethanol, acetic acid.
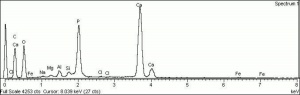
| Composition | Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1306-06-5 |
| Melting Point | 1670 C |
| Density | 3.18 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 1004.69 |
| Refractive Index | 1.63 |
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1741