Difference between revisions of "Cerussite"
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
normal lead carbonate; natural lead carbonate; horn silver; Cerussit (Deut.); Weißbleierz (Deut.); cérusite (Fr.); cerusita (Esp.); albayalde (Esp.); carbonato de plomo (Esp.); cerussite (It.); cerusite (Port.); cerussiet (Ned.) | normal lead carbonate; natural lead carbonate; horn silver; Cerussit (Deut.); Weißbleierz (Deut.); cérusite (Fr.); cerusita (Esp.); albayalde (Esp.); carbonato de plomo (Esp.); cerussite (It.); cerusite (Port.); cerussiet (Ned.) | ||
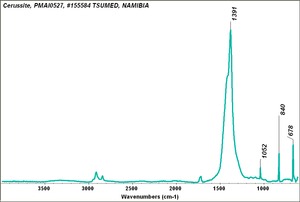
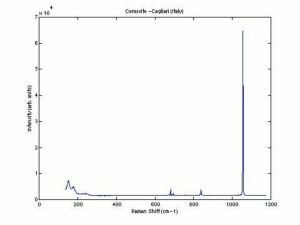
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Cerussiteitaly1.jpg~Raman]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Cerussite PMA.TIF~FTIR (PMA)|Cerussiteitaly1.jpg~Raman]]] |
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| − | + | * Toxic. Carcinogen, teratogen, suspected mutagen | |
| − | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | |
| − | Ground particle are transparent under plane polarized light. High birefringence under cross polars with fourth order interference colors. Extinction is complete | + | * Orthorhombic crystal system with tabular, prismatic or pyramidal crystals. |
| + | * Brittle with conchoidal fracture. | ||
| + | * Yellowish to golden fluorescence. | ||
| + | * Can be transparent to translucent. | ||
| + | * Luster = adamantine to silky. | ||
| + | * Streak = white. | ||
| + | * Effervescent in acids. | ||
| + | * Ground particle are transparent under plane polarized light. | ||
| + | * High birefringence under cross polars with fourth order interference colors. Extinction is complete | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 29: | Line 37: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 6.55 | + | | 6.55 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| Line 35: | Line 43: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | + | * R.J.Gettens, H. Kuhn, and W.T. Chase, "Lead White", ''Artists Pigments'', Volume 2, A. Roy (ed.), Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1993. | |
| − | + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Cerussite.shtml Cerussite] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 Comment: Vol 2, page 301 | * Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 Comment: Vol 2, page 301 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: cerussite" | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: cerussite" [Accessed December 4, 2001]. |
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 Comment: source for physical parameters | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 Comment: source for physical parameters | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cerussite (Accessed Sept 2 2005, Mons=3-3.75, spec. grav=6.5) |
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
Latest revision as of 08:02, 28 May 2022
Description
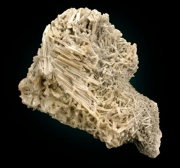
A grayish-white, crystalline mineral composed of lead carbonate. Cerussite, first described by K. Gesner in 1565, is one of the primary types of lead ore. It is mined in Spain (Murcia), England (Cornwall), Saxony (Johanngerogenstadt), Namibia (Tsumeb), Australia (New South Wales), Canada (British Columbia) and the U.S.(Colorado, Arizona, New Mexico, Idaho, Pennsylvania). Cerussite can be formed by the action of ground water on Galena (lead sulfide) ore. Although basic lead carbonate has been used as a white pigment since ancient times, it was made synthetically and not obtained from the naturally occurring cerussite ore. In fact, cerussite has rarely been used as a white pigment although it is occasionally found as an impurity in basic lead carbonate (Gettens, Kuhn and Chase, 1993).
Synonyms and Related Terms
normal lead carbonate; natural lead carbonate; horn silver; Cerussit (Deut.); Weißbleierz (Deut.); cérusite (Fr.); cerusita (Esp.); albayalde (Esp.); carbonato de plomo (Esp.); cerussite (It.); cerusite (Port.); cerussiet (Ned.)
Risks
- Toxic. Carcinogen, teratogen, suspected mutagen
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Orthorhombic crystal system with tabular, prismatic or pyramidal crystals.
- Brittle with conchoidal fracture.
- Yellowish to golden fluorescence.
- Can be transparent to translucent.
- Luster = adamantine to silky.
- Streak = white.
- Effervescent in acids.
- Ground particle are transparent under plane polarized light.
- High birefringence under cross polars with fourth order interference colors. Extinction is complete
| Composition | PbCO3 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 3.0 - 3.5 |
| Density | 6.55 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.803; 2.074; 2.076 |
Resources and Citations
- R.J.Gettens, H. Kuhn, and W.T. Chase, "Lead White", Artists Pigments, Volume 2, A. Roy (ed.), Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1993.
- Mineralogy Database: Cerussite
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 Comment: Vol 2, page 301
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: cerussite" [Accessed December 4, 2001].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 Comment: source for physical parameters
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cerussite (Accessed Sept 2 2005, Mons=3-3.75, spec. grav=6.5)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998