Difference between revisions of "Cobaltic oxide"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:Cobalt black C100x.jpg|thumb|Cobalt black]] | + | [[File:Cobalt black C100x.jpg|thumb|Cobalt black at 100x (visible light left; UV light right)]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
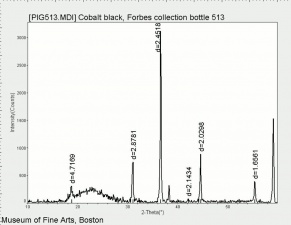
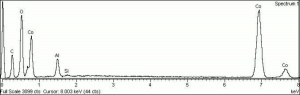
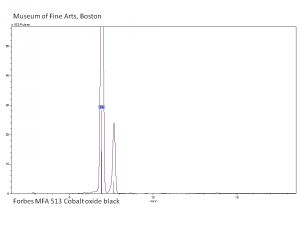
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|PIG513.jpg~XRD|f513sem.jpg~SEM|f513edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide16 F513.PNG~XRF]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|PIG513.jpg~XRD|f513sem.jpg~SEM|f513edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide16 F513.PNG~XRF]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| − | Soluble in concentrated acids. Insoluble in water. | + | * Skin contact may cause allergies, especially on elbows, neck and ankles. |
| + | * Chronic inhalation may cause asthma. | ||
| + | * Ingestion may cause vomiting, diarrhea and the sensation of hotness. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Soluble in concentrated acids. Insoluble in water. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 23: | Line 29: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 895 (dec) | + | | 895 C (dec) |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 4.81-5.60 | + | | 4.81-5.60 g/ml |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | * Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | ||
Latest revision as of 12:18, 30 May 2022
Description
A naturally occurring black powder. Cobaltic oxide is used to give a brilliant blue color glaze and enamel. Cobalt oxide was used as a blue colorant in ceramic glazes and underglazes since at least the 8th century in the Middle East. It became very popular in the 14th century when it was used for Ming Dynasty ceramics. Cobaltic oxide is not used as a black paint pigment.
Synonyms and Related Terms
cobalt black; cobalt oxide; óxido de cobalto (Esp., Port.); oxyde de cobalt (Fr.); ossido cobaltico (It.); black oxide of cobalt; cobalt blue glaze
Risks
- Skin contact may cause allergies, especially on elbows, neck and ankles.
- Chronic inhalation may cause asthma.
- Ingestion may cause vomiting, diarrhea and the sensation of hotness.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in concentrated acids. Insoluble in water.
| Composition | Co2O3 or Co3O4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1308-04-9 |
| Melting Point | 895 C (dec) |
| Density | 4.81-5.60 g/ml |
Resources and Citations
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993