Difference between revisions of "Pectin"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
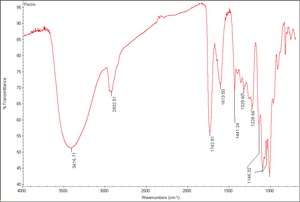
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Pectin.TIF~FTIR(MFA)]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Pectin.TIF~FTIR(MFA)]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/64240.htm MSDS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
Soluble in water. Insoluble in organic solvents. | Soluble in water. Insoluble in organic solvents. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 23: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 | ||
Revision as of 13:28, 8 September 2022
Description
A generic term for a group of polysaccharides that are located in the cell walls of all plant tissues. Pectin is composed of methoxylated galacturonic acids joined in long chains. The main commercial sources of pectin are citrus peel and apple pomace. Pectin dissolves in water to produce viscous stable solutions. They are mainly used for food products (jams and jellies) but are also found as sizing agents in paper and textiles.
Synonyms and Related Terms
pectina (Esp.); pectine (Fr.); pectina (It)
Risks
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water. Insoluble in organic solvents.
| CAS | 9000-69-5 |
|---|
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 7194
- Mary-Lou Florian, Dale Paul Kronkright, Ruth E. Norton, The Conservation of Artifacts Made from Plant Materials, The Getty Conservation Institute, Los Angeles, 1990
- Bernard Toale, The Art of Papermaking, Davis Publications, Portland OR, 1983
- I.W. Cottrell, J.K. Baird, gums chapter