Difference between revisions of "Polyvinyl chloride fiber"
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| + | |||
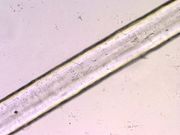
| + | [[File:63 polyvinylchl 200X.jpg|thumb|Polyvinyl chloride fiber,200x]] | ||
| + | [[File:63 polyvinylchl 200X pol.jpg|thumb|Polyvinyl chloride fiber, 200x polarized light]] | ||
A manufactured fiber in which the fiber-forming substance is any long chain synthetic polymer composed of at least 85% by weight of vinyl chloride units (Federal Trade Commission definition). PVC fibers are generically known as vinyon fibers or chlorofibers. Pure PVC fibers are used to make elastomeric fabrics. They are also used in outdoor fabrics, such as tarps, awnings, rain gear and fishing nets. | A manufactured fiber in which the fiber-forming substance is any long chain synthetic polymer composed of at least 85% by weight of vinyl chloride units (Federal Trade Commission definition). PVC fibers are generically known as vinyon fibers or chlorofibers. Pure PVC fibers are used to make elastomeric fabrics. They are also used in outdoor fabrics, such as tarps, awnings, rain gear and fishing nets. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 11: | ||
polyvinylchloride fibre; poly(vinyl chloride); vinyon; chlorofiber; Fibravyl [Rhone-Poulenc Textile, France]; Rhovyl, Thermovyl; Leavin [ACSA, Italy]; Cordelan; Movil [Societa Polymer, Italy]; Vinagel; Elaston; Trovidur; Bexan [BX Plastics]; Bristrand [Polymers Inc.]; Pe-Ce-U [Farbenfabriken Bayer A.G.; Tricovil; Kubo | polyvinylchloride fibre; poly(vinyl chloride); vinyon; chlorofiber; Fibravyl [Rhone-Poulenc Textile, France]; Rhovyl, Thermovyl; Leavin [ACSA, Italy]; Cordelan; Movil [Societa Polymer, Italy]; Vinagel; Elaston; Trovidur; Bexan [BX Plastics]; Bristrand [Polymers Inc.]; Pe-Ce-U [Farbenfabriken Bayer A.G.; Tricovil; Kubo | ||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| − | + | * Degrades with heat and light to produce hydrochloric acid. | |
| − | + | * May also form carbon monoxide or phosgene. | |
| − | + | * Develops a negative static charge. | |
| − | + | * CDH Fine Chemicals: [https://www.cdhfinechemical.com/images/product/msds/37_1117586839_POLYVINYLCHLORIDECASNO9002-86-2MSDS.pdf SDS] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== |
| − | + | * Soluble in chlorinated hydrocarbons and aromatic solvents. | |
| − | + | * Insoluble in water, alcohols, concentrated acids and alkalis. | |
| − | + | * Burns with green smoky flame and evolves HCl; extinguishes when removed form flame source. | |
| − | + | * Cross section = irregular. | |
| − | + | * Properties of 100% PVC: Tenacity = 2.7-3.0 g/denier (dry or wet) elongation 12-20% (dry or wet) Moisture regain = 0 %. | |
| + | * Melting Point = 160 | ||
| + | * Density = 1.38-1.40 g/ml | ||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 36: | Line 34: | ||
[[media:download_file_90.pdf|Fiber Burn Tests]] | [[media:download_file_90.pdf|Fiber Burn Tests]] | ||
| − | + | == Resources and Citations == | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
* Hoechst Celanese Corporation, ''Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology'' (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990 | * Hoechst Celanese Corporation, ''Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology'' (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990 | ||
| − | * J.Gordon Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres'', Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England | + | * J.Gordon Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres'', 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984, p.444. |
| − | * F. Kidd, ''Brushmaking Materials'', | + | * F. Kidd, ''Brushmaking Materials'', British Brush Manufacturers, London, 1957 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:47, 27 September 2022
Description
A manufactured fiber in which the fiber-forming substance is any long chain synthetic polymer composed of at least 85% by weight of vinyl chloride units (Federal Trade Commission definition). PVC fibers are generically known as vinyon fibers or chlorofibers. Pure PVC fibers are used to make elastomeric fabrics. They are also used in outdoor fabrics, such as tarps, awnings, rain gear and fishing nets.
See Vinyon fiber.
Synonyms and Related Terms
polyvinylchloride fibre; poly(vinyl chloride); vinyon; chlorofiber; Fibravyl [Rhone-Poulenc Textile, France]; Rhovyl, Thermovyl; Leavin [ACSA, Italy]; Cordelan; Movil [Societa Polymer, Italy]; Vinagel; Elaston; Trovidur; Bexan [BX Plastics]; Bristrand [Polymers Inc.]; Pe-Ce-U [Farbenfabriken Bayer A.G.; Tricovil; Kubo
Risks
- Degrades with heat and light to produce hydrochloric acid.
- May also form carbon monoxide or phosgene.
- Develops a negative static charge.
- CDH Fine Chemicals: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in chlorinated hydrocarbons and aromatic solvents.
- Insoluble in water, alcohols, concentrated acids and alkalis.
- Burns with green smoky flame and evolves HCl; extinguishes when removed form flame source.
- Cross section = irregular.
- Properties of 100% PVC: Tenacity = 2.7-3.0 g/denier (dry or wet) elongation 12-20% (dry or wet) Moisture regain = 0 %.
- Melting Point = 160
- Density = 1.38-1.40 g/ml
Comparisons
Properties of Synthetic Fibers
Resources and Citations
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres, 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984, p.444.
- F. Kidd, Brushmaking Materials, British Brush Manufacturers, London, 1957