Difference between revisions of "Milk"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Description == | ||
| + | |||
| + | A nutritional liquid produced by female mammary glands to feed newborn mammals. Milk from domesticated animals (cows, goats, sheep) has been used as a human food source, either directly or as processed into butter and cheese. Milk is essentially an emulsion of | ||
| + | [[fat|fat]] (4%) and | ||
| + | [[protein|protein]] (3%) in water, along with dissolved sugar ( | ||
| + | [[lactose|lactose]]), minerals ( | ||
| + | [[calcium|calcium]], | ||
| + | [[phosphorus|phosphorus]]), and vitamins (B, C and D). | ||
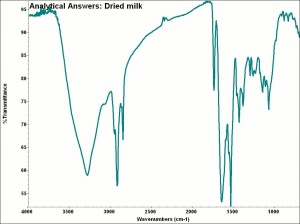
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiCHEESE.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiCHEESE.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:34, 18 October 2022
Description
A nutritional liquid produced by female mammary glands to feed newborn mammals. Milk from domesticated animals (cows, goats, sheep) has been used as a human food source, either directly or as processed into butter and cheese. Milk is essentially an emulsion of
Fat (4%) and
Protein (3%) in water, along with dissolved sugar (
Lactose), minerals (
Calcium,
Phosphorus), and vitamins (B, C and D).