Difference between revisions of "Orthoclase"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Potashfeldsparemr1.jpg|thumb|Orthoclase (potassium feldspar)]] | [[File:Potashfeldsparemr1.jpg|thumb|Orthoclase (potassium feldspar)]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
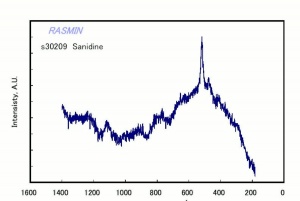
| − | + | [[File:ps30209sanidine.jpg|thumb|Sanidine]] | |
A common type of [[feldspar|feldspar]] composed of potassium aluminum silicate. Orthoclase is found in many igneous rocks worldwide. It is generally a white or pale pink in color and has two good cleavage planes at right angles. Pure orthoclase is called adularia. Orthoclase with an intergrowth of albite has a pearly opalescence and is called [[moonstone|moonstone]]. It is used as a gemstone. Sanidine is a glassy type of orthoclase. Orthoclase has been used since ancient times for beads. It is also used in the manufacture of glass, porcelain and enamels. | A common type of [[feldspar|feldspar]] composed of potassium aluminum silicate. Orthoclase is found in many igneous rocks worldwide. It is generally a white or pale pink in color and has two good cleavage planes at right angles. Pure orthoclase is called adularia. Orthoclase with an intergrowth of albite has a pearly opalescence and is called [[moonstone|moonstone]]. It is used as a gemstone. Sanidine is a glassy type of orthoclase. Orthoclase has been used since ancient times for beads. It is also used in the manufacture of glass, porcelain and enamels. | ||
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
potash feldspar; adularia; moonstone; sanidine; microcline; amazonstone; amazonite; ortoclasa (Esp.); orthoclase(Fr.); ortose (Port.); Orthoklas (Deut.); orthoclaas (Ned.) | potash feldspar; adularia; moonstone; sanidine; microcline; amazonstone; amazonite; ortoclasa (Esp.); orthoclase(Fr.); ortose (Port.); Orthoklas (Deut.); orthoclaas (Ned.) | ||
| − | |||
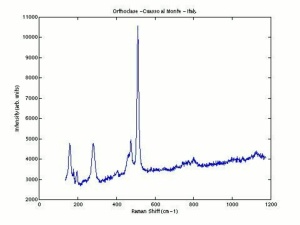
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Orthoclaseitaly1.jpg~Raman|sanidineRS.jpg~Raman]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Orthoclaseitaly1.jpg~Raman|sanidineRS.jpg~Raman]]] | ||
==Physical and Chemical Properties == | ==Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | Monoclinic system; twinned crystals common. Perfect cleavage in two directions (right angles). Fracture = uneven. Luster = vitreous. Streak = white. | + | * Monoclinic system; twinned crystals common. |
| + | * Perfect cleavage in two directions (right angles). | ||
| + | * Fracture = uneven. | ||
| + | * Luster = vitreous. | ||
| + | * Streak = white. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 2.56-2.58 | + | | 2.56-2.58 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
Revision as of 15:42, 20 October 2022
Description
A common type of Feldspar composed of potassium aluminum silicate. Orthoclase is found in many igneous rocks worldwide. It is generally a white or pale pink in color and has two good cleavage planes at right angles. Pure orthoclase is called adularia. Orthoclase with an intergrowth of albite has a pearly opalescence and is called Moonstone. It is used as a gemstone. Sanidine is a glassy type of orthoclase. Orthoclase has been used since ancient times for beads. It is also used in the manufacture of glass, porcelain and enamels.
Synonyms and Related Terms
potash feldspar; adularia; moonstone; sanidine; microcline; amazonstone; amazonite; ortoclasa (Esp.); orthoclase(Fr.); ortose (Port.); Orthoklas (Deut.); orthoclaas (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Monoclinic system; twinned crystals common.
- Perfect cleavage in two directions (right angles).
- Fracture = uneven.
- Luster = vitreous.
- Streak = white.
| Composition | KAlSi3O8 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 6.0 - 6.5 |
| Density | 2.56-2.58 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.52 |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Gemstones
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Orthoclase
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "orthoclase" [Accessed December 4, 2001]
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orthoclase (Accessed Sept. 14, 2005)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 316
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998