Difference between revisions of "Cornstarch"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
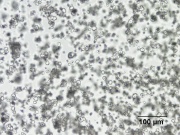
| − | [[File:2_Cornstarch_200XS.jpg|thumb|Cornstarch]] | + | [[File:2_Cornstarch_200XS.jpg|thumb|Cornstarch at 200x]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
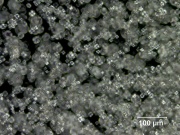
| − | + | [[File:2_Cornstarch_200XS_pol.jpg|thumb|Cornstarch at 200x polarized light]] | |
White amorphous [[polysaccharide]] granules that compose about 70% of a [[corn]] kernel. Cornstarch is separated from the [[gluten]] and fibrous particles by sieving, wet grinding, then wash flotation. It is composed of 28% [[amylose]] and 75% [[amylopectin]]. When heated with water, cornstarch forms a medium viscosity solution that does not change with heating time. It thickens substantially on cooling to form an opaque gel. Cornstarch is the predominant starch used in North America as a thickener and filler in foods. It is used as an absorbent powder in baby powders and on the interior of some powdered latex gloves. Cornstarch is also used as an adhesive, a sizing agent, and a filler in waxes and plastics. | White amorphous [[polysaccharide]] granules that compose about 70% of a [[corn]] kernel. Cornstarch is separated from the [[gluten]] and fibrous particles by sieving, wet grinding, then wash flotation. It is composed of 28% [[amylose]] and 75% [[amylopectin]]. When heated with water, cornstarch forms a medium viscosity solution that does not change with heating time. It thickens substantially on cooling to form an opaque gel. Cornstarch is the predominant starch used in North America as a thickener and filler in foods. It is used as an absorbent powder in baby powders and on the interior of some powdered latex gloves. Cornstarch is also used as an adhesive, a sizing agent, and a filler in waxes and plastics. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 10: | Line 8: | ||
corn starch; cornflour; maïzena (Ned.); | corn starch; cornflour; maïzena (Ned.); | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Susceptible to biodeterioration. | |
| + | * Dried films become brittle with age. | ||
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://beta-static.fishersci.com/content/dam/fishersci/en_US/documents/programs/education/regulatory-documents/sds/chemicals/chemicals-c/S25580.pdfSDS] | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
| − | + | * Rectangular, slightly concave particles. Granule size = 5 - 26 micrometers. | |
| + | * Gelatinization temperature = 62 - 72C. | ||
| + | * Reacts with a iodine/potassium iodide solution to give a positive purple color | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 766 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 766 | ||
| Line 34: | Line 32: | ||
* Book and Paper Group, ''Paper Conservation Catalog'', AIC, 1984, 1989 | * Book and Paper Group, ''Paper Conservation Catalog'', AIC, 1984, 1989 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "cereal processing" | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "cereal processing" [Accessed April 8, 2002] |
* Irving Skeist, ''Handbook of Adhesives'', Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977 | * Irving Skeist, ''Handbook of Adhesives'', Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cornstarch (Accessed Mar. 1, 2006) |
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
Latest revision as of 16:04, 22 October 2022
Description
White amorphous Polysaccharide granules that compose about 70% of a Corn kernel. Cornstarch is separated from the Gluten and fibrous particles by sieving, wet grinding, then wash flotation. It is composed of 28% Amylose and 75% Amylopectin. When heated with water, cornstarch forms a medium viscosity solution that does not change with heating time. It thickens substantially on cooling to form an opaque gel. Cornstarch is the predominant starch used in North America as a thickener and filler in foods. It is used as an absorbent powder in baby powders and on the interior of some powdered latex gloves. Cornstarch is also used as an adhesive, a sizing agent, and a filler in waxes and plastics.
Synonyms and Related Terms
corn starch; cornflour; maïzena (Ned.);
Risks
- Susceptible to biodeterioration.
- Dried films become brittle with age.
- Fisher Scientific: [1]
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Rectangular, slightly concave particles. Granule size = 5 - 26 micrometers.
- Gelatinization temperature = 62 - 72C.
- Reacts with a iodine/potassium iodide solution to give a positive purple color
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 766
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "cereal processing" [Accessed April 8, 2002]
- Irving Skeist, Handbook of Adhesives, Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cornstarch (Accessed Mar. 1, 2006)
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998