Difference between revisions of "Sustainable materials"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
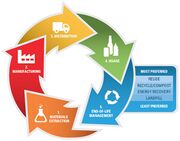
| − | + | [[File:EPA Materials lifecycle.jpg|thumb|EPA's Life cycle of materials and products from material extraction, manufacturing, distribution, use and end of life management]] | |
| + | ==Description== | ||
| + | (EPA) "Sustainable materials management (SMM) is a systematic approach to using and reusing materials more productively over their entire life cycles. It represents a change in how our society thinks about the use of natural resources and environmental protection. By examining how materials are used throughout their life cycle, an SMM approach seeks to: | ||
| + | * Use materials in the most productive way with an emphasis on using less. | ||
| + | * Reduce toxic chemicals and environmental impacts throughout the material life cycle. | ||
| + | * Assure we have sufficient resources to meet today’s needs and those of the future. | ||
| + | By looking at a product's entire life cycle—from materials extraction to end-of-life management—we can find new opportunities to reduce environmental impacts, conserve resources, and reduce costs. For example, a product may be re-designed so it is manufactured using different, fewer, less toxic and more durable materials. It is designed so that at the end of its useful life it can be readily disassembled. The product’s manufacturer maintains a relationship with its customers to ensure best use of the product, its maintenance and return at end-of-life. This helps the manufacturer identify changing needs of their customers, create customer loyalty, and reduce material supply risk. Further, the manufacturer has a similar relationship with its suppliers, which helps the manufacturer respond more quickly to changing demands, including reducing environmental impacts along the supply chain." | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sustainable materials are optimal for people, objects, and the environment. Their careful selection, use, and disposal has both a direct as well as a broad impact on the economic and environmental future of the world. Without change, the globe will be resource-constrained. | ||
| − | + | See also [[recycling]] and [[Red list of Materials]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Sustainability; Green materials | Sustainability; Green materials | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Resources and Citations== | ==Resources and Citations== | ||
| − | * Cambridge Seven: [https://issuu.com/oneamongseven/docs/sed_c_toolkit_web_version_c7a Sustainable Exhibition Design & Construction Toolkit] | + | * EPA: [https://www.epa.gov/smm/sustainable-materials-management-basics Sustainable Materials Management] Accessed Nov. 2023 |
| − | * Life Cycle Assessment Project - Wiki at www.conservation-wiki.com. Accessed Nov. 2023 | + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sustainable_materials_management Sustainable Materials Management] Accessed Nov. 2023 |
| + | * Cambridge Seven: [https://issuu.com/oneamongseven/docs/sed_c_toolkit_web_version_c7a Sustainable Exhibition Design & Construction Toolkit] Accessed Nov. 2023 | ||
| + | * Life Cycle Assessment Project - Wiki at www.conservation-wiki.com. Accessed Nov. 2023 | ||
* "STiCH" at stich.culturalheritage.org. Accessed Nov. 2023. | * "STiCH" at stich.culturalheritage.org. Accessed Nov. 2023. | ||
* "Simple sustainability practices in Conservation – What can you do?". Australian Institute for the Conservation of Cultural Material. [https://aiccm.org.au/network-news/simple-sustainability-practices-in-conservation-what-can-you-do/ Link] | * "Simple sustainability practices in Conservation – What can you do?". Australian Institute for the Conservation of Cultural Material. [https://aiccm.org.au/network-news/simple-sustainability-practices-in-conservation-what-can-you-do/ Link] | ||
* Megan de Silva, Jane Henderson,"Sustainability in conservation practice". Journal of the Institute of Conservation. 34 (1): 5–15, 2011. | * Megan de Silva, Jane Henderson,"Sustainability in conservation practice". Journal of the Institute of Conservation. 34 (1): 5–15, 2011. | ||
| − | [[Category:Materials database]] [[Category:MWG]] | + | [[Category:Materials database]] [[Category:MWG]] [[Category: Climate/Environment]] |
Latest revision as of 11:54, 3 November 2023
Description
(EPA) "Sustainable materials management (SMM) is a systematic approach to using and reusing materials more productively over their entire life cycles. It represents a change in how our society thinks about the use of natural resources and environmental protection. By examining how materials are used throughout their life cycle, an SMM approach seeks to:
- Use materials in the most productive way with an emphasis on using less.
- Reduce toxic chemicals and environmental impacts throughout the material life cycle.
- Assure we have sufficient resources to meet today’s needs and those of the future.
By looking at a product's entire life cycle—from materials extraction to end-of-life management—we can find new opportunities to reduce environmental impacts, conserve resources, and reduce costs. For example, a product may be re-designed so it is manufactured using different, fewer, less toxic and more durable materials. It is designed so that at the end of its useful life it can be readily disassembled. The product’s manufacturer maintains a relationship with its customers to ensure best use of the product, its maintenance and return at end-of-life. This helps the manufacturer identify changing needs of their customers, create customer loyalty, and reduce material supply risk. Further, the manufacturer has a similar relationship with its suppliers, which helps the manufacturer respond more quickly to changing demands, including reducing environmental impacts along the supply chain."
Sustainable materials are optimal for people, objects, and the environment. Their careful selection, use, and disposal has both a direct as well as a broad impact on the economic and environmental future of the world. Without change, the globe will be resource-constrained.
See also Recycling and Red list of Materials.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Sustainability; Green materials
Resources and Citations
- EPA: Sustainable Materials Management Accessed Nov. 2023
- Wikipedia: Sustainable Materials Management Accessed Nov. 2023
- Cambridge Seven: Sustainable Exhibition Design & Construction Toolkit Accessed Nov. 2023
- Life Cycle Assessment Project - Wiki at www.conservation-wiki.com. Accessed Nov. 2023
- "STiCH" at stich.culturalheritage.org. Accessed Nov. 2023.
- "Simple sustainability practices in Conservation – What can you do?". Australian Institute for the Conservation of Cultural Material. Link
- Megan de Silva, Jane Henderson,"Sustainability in conservation practice". Journal of the Institute of Conservation. 34 (1): 5–15, 2011.