Difference between revisions of "Benzene"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A clear, colorless, volatile aromatic solvent. Benzene was first isolated by Faraday in 1825. It is obtained from the destructive distillation of [ | + | A clear, colorless, volatile aromatic solvent. Benzene was first isolated by Faraday in 1825. It is obtained from the destructive distillation of [[coal]] and [[oil]]. The industrial grade distillation fraction sold as [[benzol]] contains about 65% benzene, 33% [[toluene]] plus 2% other aromatic compounds. Benzene was formerly a commonly used solvent for [[wax|waxes]], [[natural%20resin|resins]], [[oil|oils]], [[rubber (synthetic)|rubber]], and [[paint%20remover|paint removers]], but this was discontinued because of its toxicity. It is now used primarily for the manufacture of styrene polymers, aromatic chlorides, and some dyes. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|benzene.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|benzene.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| − | == | + | * Known carcinogen. Toxic in ingestion and inhalation. |
| + | * Skin contact causes irritation and dissolves fat. | ||
| + | * Flammable and explosive. Dangerous fire risk. Burns with a sooty flame. | ||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/02610.htm MSDS] | ||
| + | * EPA lists benzene as hazardous waste; concentrations over 10% must be disposed of appropriately | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Miscible with ethanol, ether, acetone, carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide, acetic acid, oils. Slightly soluble in water. | Miscible with ethanol, ether, acetone, carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide, acetic acid, oils. Slightly soluble in water. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 29: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 5.5 | + | | 5.5 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 0.8787 | + | | 0.8787 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 35: | Line 41: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ||
| − | | 80.1 | + | | 80.1 C |
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
[[media:download_file_116.pdf|Properties of Common Solvents]] | [[media:download_file_116.pdf|Properties of Common Solvents]] | ||
| − | + | == Resources and Citations == | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | * | + | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 |
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1094 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1094 | ||
| − | * | + | * Hoechst Celanese Corporation, ''Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology'' (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990 |
| − | * | + | * Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 |
| − | * | + | * Reed Kay, ''The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials'', Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983 |
| − | * | + | * Michael McCann, ''Artist Beware'', Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:19, 17 April 2024
Description
A clear, colorless, volatile aromatic solvent. Benzene was first isolated by Faraday in 1825. It is obtained from the destructive distillation of Coal and Oil. The industrial grade distillation fraction sold as Benzol contains about 65% benzene, 33% Toluene plus 2% other aromatic compounds. Benzene was formerly a commonly used solvent for waxes, resins, oils, rubber, and paint removers, but this was discontinued because of its toxicity. It is now used primarily for the manufacture of styrene polymers, aromatic chlorides, and some dyes.
Synonyms and Related Terms
benzol; cyclohexatriene
Risks
- Known carcinogen. Toxic in ingestion and inhalation.
- Skin contact causes irritation and dissolves fat.
- Flammable and explosive. Dangerous fire risk. Burns with a sooty flame.
- ThermoFisher: MSDS
- EPA lists benzene as hazardous waste; concentrations over 10% must be disposed of appropriately
Physical and Chemical Properties
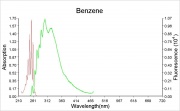
Miscible with ethanol, ether, acetone, carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide, acetic acid, oils. Slightly soluble in water.
| Composition | C6H6 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 71-43-2 |
| Melting Point | 5.5 C |
| Density | 0.8787 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 78.1 |
| Refractive Index | 1.50110 |
| Boiling Point | 80.1 C |
Comparisons
Resources and Citations
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1094
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979