Difference between revisions of "Barley starch"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
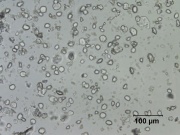
| − | [[File:4_Barley_starch_200XS.jpg|thumb|Barley starch]] | + | [[File:4_Barley_starch_200XS.jpg|thumb|Barley starch at 200x]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
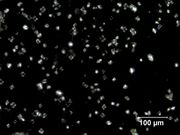
| − | + | [[File:4_Barley_starch_200XS_pol.jpg|thumb|Barley starch at 200x<br>Polarized light]] | |
| − | The milled product of [ | + | The milled product of [[barley]] grains obtained from barley plants, ''Hordeum vulgare'' (6-rowed) or ''Hordeum distichon'' (2-rowed). Barley was cultivated in Ethipia and southeast Asia since prehistoric times. From biblical times through the Middle Ages, barley was the primary grain for producing unleavened bread and porridge throughout Europe, the Middle East, Egypt, and some parts of Asia. The grains are also been used to make malt beer. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | Hordeum vulgare (6-rowed); ''Hordeum distichon'' (2-rowed | + | Hordeum vulgare (6-rowed); ''Hordeum distichon'' (2-rowed |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 |
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', https://www.britannica.com/topic/Britannica-Online Comment: "Barley." Accessed 15 July 2004. |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:29, 2 May 2022
Description
The milled product of Barley grains obtained from barley plants, Hordeum vulgare (6-rowed) or Hordeum distichon (2-rowed). Barley was cultivated in Ethipia and southeast Asia since prehistoric times. From biblical times through the Middle Ages, barley was the primary grain for producing unleavened bread and porridge throughout Europe, the Middle East, Egypt, and some parts of Asia. The grains are also been used to make malt beer.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Hordeum vulgare (6-rowed); Hordeum distichon (2-rowed
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Encyclopedia Britannica, https://www.britannica.com/topic/Britannica-Online Comment: "Barley." Accessed 15 July 2004.