Difference between revisions of "Biotin"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A white crystalline compound that acts as a vitamin. Biotin is part of the B complex of vitamins. It influences fat metabolism and growth rates. Biotin is synthesized in the intestinal tract of humans. It is highly concentrated in the liver, kidney, pancreas, [ | + | A white crystalline compound that acts as a vitamin. Biotin is part of the B complex of vitamins. It influences fat metabolism and growth rates. Biotin is synthesized in the intestinal tract of humans. It is highly concentrated in the liver, kidney, pancreas, [[milk]], and [[egg yolk]]. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
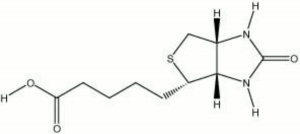
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|biotin.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|biotin.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=BP2321&productDescription=BIOTIN+1GR&vendorId=VN00033897&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
Soluble in water, ethanol. Insoluble in naphtha, chloroform. | Soluble in water, ethanol. Insoluble in naphtha, chloroform. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 27: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 230-232 | + | | 230-232 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 29: | Line 33: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 853 |
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
| − | * | + | * Richard C. Wolbers, Nanette T. Sterman, Chris Stavroudis, ''Notes for Workshop on New Methods in the Cleaning of Paintings'', J.Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 1990 |
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1272 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1272 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biotin (Accessed Oct. 18, 2005) |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:25, 4 May 2022
Description
A white crystalline compound that acts as a vitamin. Biotin is part of the B complex of vitamins. It influences fat metabolism and growth rates. Biotin is synthesized in the intestinal tract of humans. It is highly concentrated in the liver, kidney, pancreas, Milk, and Egg yolk.
Synonyms and Related Terms
vitamin H; vitamin B7; hexahydro-2-oxo-1H-thieno [3,4-d] imidazole-4-pentanoic acid; biotine (Fr., Ned.); Vitamine B8 (Fr.); biotina (It.); Vitamina H (It.); biotyna (Pol.); Biotin (Deut., Sven.)
Risks
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water, ethanol. Insoluble in naphtha, chloroform.
| Composition | C10H16N2O3S |
|---|---|
| CAS | 58-85-5 |
| Melting Point | 230-232 C |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 244.32 |
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 853
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Richard C. Wolbers, Nanette T. Sterman, Chris Stavroudis, Notes for Workshop on New Methods in the Cleaning of Paintings, J.Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 1990
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1272
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biotin (Accessed Oct. 18, 2005)