Difference between revisions of "Western hemlock"
(username removed) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:10_W.CoastHemlock.jpg|thumb|West Coast Hemlock | + | [[File:10_W.CoastHemlock.jpg|thumb|West Coast Hemlock (''Tsuga heterophylla'')]] |
| − | |||
| − | (''Tsuga heterophylla'')]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A strong, tall hemlock, Tsuga | + | A strong, tall hemlock, ''Tsuga heterophylla'', native to the northwestern Pacific coast of Canada and the U.S. The western hemlock produces a soft, lightweight wood with a straight, fine grain. Peak production was in 1927. The lumber was used for millwork, construction, boxes, fences, and boats. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | Pacific hemlock; west coast hemlock; | + | ''Tsuga heterophylla''; Pacific hemlock; west coast hemlock; werstern hemlock-spruce; hemlock fir; Prince Albert's hemlock |
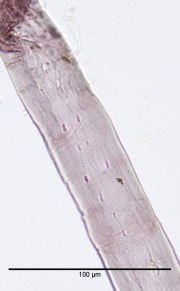
| + | [[File:W hemlock 40x pits2label.jpg|thumb|Western Hemlock fiber stained with Graff "C" Stain]] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| + | * Height = 50-70 m, diameter up to 3m; branches are drooping | ||
| + | * Bark = thin, brown with furrows | ||
| + | * Leaves = needles are 5-23 mm long and 1.5-2 mm wide | ||
| + | * Density = 28 pcf | ||
| + | * Cones = small, cylindrical (14-20 mm long) | ||
| + | * Density = 28 pcf | ||
| − | + | Paper fiber type: softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified by the presence of small piceoid and cupressiod ray parenchyma pits. Ray tracheids are non-dentate and usually collapsed. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: varies with pulping method. Average dimensions of fibers: length, 4.2mm; width, 30-40 μm. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]] (sulfate) and [[sulfite process|sulfite]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 394 |
* ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | * ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | ||
| − | * | + | * External source or communication Comment: West Coast Lumbermen's Association, Seattle, Wash.: air-dry weight = 28 pcf |
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "hemlock." | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "hemlock." Accessed: 19 Oct. 2004 . |
| + | * Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. ''Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science)''. Springer, 1995. | ||
| + | * Walter Rantanen. 'Fiber ID Course.' Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture. | ||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:50, 8 October 2020
Description
A strong, tall hemlock, Tsuga heterophylla, native to the northwestern Pacific coast of Canada and the U.S. The western hemlock produces a soft, lightweight wood with a straight, fine grain. Peak production was in 1927. The lumber was used for millwork, construction, boxes, fences, and boats.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Tsuga heterophylla; Pacific hemlock; west coast hemlock; werstern hemlock-spruce; hemlock fir; Prince Albert's hemlock
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Height = 50-70 m, diameter up to 3m; branches are drooping
- Bark = thin, brown with furrows
- Leaves = needles are 5-23 mm long and 1.5-2 mm wide
- Density = 28 pcf
- Cones = small, cylindrical (14-20 mm long)
- Density = 28 pcf
Paper fiber type: softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified by the presence of small piceoid and cupressiod ray parenchyma pits. Ray tracheids are non-dentate and usually collapsed. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: varies with pulping method. Average dimensions of fibers: length, 4.2mm; width, 30-40 μm. Common pulping method: kraft (sulfate) and sulfite.
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 394
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- External source or communication Comment: West Coast Lumbermen's Association, Seattle, Wash.: air-dry weight = 28 pcf
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "hemlock." Accessed: 19 Oct. 2004 .
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. 'Fiber ID Course.' Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.