Difference between revisions of "Crocidolite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:87_Crocidolite_200X adj.jpg|thumb|Crocidolite]] | + | [[File:87_Crocidolite_200X adj.jpg|thumb|Crocidolite at 200x]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:87_Crocidolite_200X_pol adj.jpg|thumb|Crocidolite at 200x polarized light]] | |
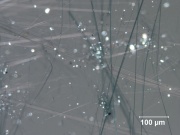
A fibrous, blue-green mineral composed of sodium iron silicate. Crocidolite is a minor commercial form of asbestos, called blue asbestos. It is found in Europe, Africa, South America and the United States. Crocidolite fibers have a harsh texture. They have fair flexibility and are strong. Crocidolite fibers are used to reinforce polymers and as heat resistant textiles. | A fibrous, blue-green mineral composed of sodium iron silicate. Crocidolite is a minor commercial form of asbestos, called blue asbestos. It is found in Europe, Africa, South America and the United States. Crocidolite fibers have a harsh texture. They have fair flexibility and are strong. Crocidolite fibers are used to reinforce polymers and as heat resistant textiles. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
blue asbestos; riebeckite; crocidolite (Port.); Krokidolit (Deut.) | blue asbestos; riebeckite; crocidolite (Port.); Krokidolit (Deut.) | ||
| − | + | == Risks == | |
| − | == | ||
| − | Fiber length = 12-300 mm (0.5 - 12 inches) Diameter = 300-350 angstroms. Luster = silky to dull.Cross section is polygonal or circular. Tensile strength = 80,000-200,00 | + | * Noncombustible. Unaffected by heat. |
| + | * Carcinogenic. | ||
| + | * Highly toxic by inhalation of dust. | ||
| + | * Skin contact cause irritation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Fiber length = 12-300 mm (0.5 - 12 inches) | ||
| + | * Diameter = 300-350 angstroms. | ||
| + | * Luster = silky to dull. | ||
| + | * Cross section is polygonal or circular. | ||
| + | * Tensile strength = 80,000-200,00 psi | ||
| + | * Resistant to alkalis and acids. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 19: | Line 30: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 3.2-3.3 | + | | 3.2-3.3 g/ml |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 |
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
Latest revision as of 14:02, 7 July 2022
Description
A fibrous, blue-green mineral composed of sodium iron silicate. Crocidolite is a minor commercial form of asbestos, called blue asbestos. It is found in Europe, Africa, South America and the United States. Crocidolite fibers have a harsh texture. They have fair flexibility and are strong. Crocidolite fibers are used to reinforce polymers and as heat resistant textiles.
Synonyms and Related Terms
blue asbestos; riebeckite; crocidolite (Port.); Krokidolit (Deut.)
Risks
- Noncombustible. Unaffected by heat.
- Carcinogenic.
- Highly toxic by inhalation of dust.
- Skin contact cause irritation.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Fiber length = 12-300 mm (0.5 - 12 inches)
- Diameter = 300-350 angstroms.
- Luster = silky to dull.
- Cross section is polygonal or circular.
- Tensile strength = 80,000-200,00 psi
- Resistant to alkalis and acids.
| Mohs Hardness | 4.0 |
|---|---|
| Density | 3.2-3.3 g/ml |
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Identification of Textile Materials, The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998