Difference between revisions of "Diopside"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:pd30241diopside.jpg|thumb|Diopside]] | [[File:pd30241diopside.jpg|thumb|Diopside]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:Diopside Aoste Wikipedia.jpg|thumb| Diopside green prismatic crystal; Image credit: Didier Descouens]] | |
| − | A green, calcium magnesium silicate mineral sometimes used as a [ | + | A green, calcium magnesium silicate mineral sometimes used as a [[gemstone]]. Diopside is a [[pyroxene]] type mineral with short, monoclinic crystals. The transparent to translucent crystals have either a square or octagonal cross section. The color of diopside crystals usually from light to dark green, but may be blue, brown, colorless or pale violet. Diopside has been found at many locations throughout Europe (Russia, Finland, Sweden, Switzerland and Italy), Canada (Ontario, Quebec) and the United States (New York, California and Maine). Powdered diopside is used as a matting agent in ceramic glazes. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | calcium magnesium silicate; diopside (Fr.); | + | calcium magnesium silicate; diopside (Fr.); diópsido (Esp., Port.); Diposid (Deut.); diopsiet (Ned.) |
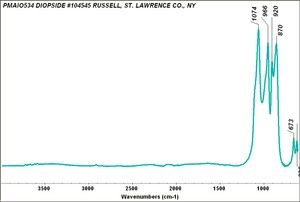
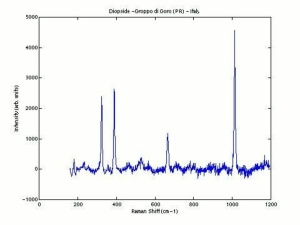
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|DIOPSIDE PMA.TIF~FTIR (PMA)|Diopsideitaly1.jpg~Raman (U of Parma)]]] | |
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign| | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Luster = vitreous to dull | + | * Monoclinic system with slender square or octagonal prisms that are often twinned |
| + | * Cleavage occurs at intersecting angles of 87 and 93 degrees | ||
| + | * Fracture = uneven to conchoidal | ||
| + | * Luster = vitreous to dull | ||
| + | * Streak = white, gray or green | ||
| + | * Fluorescence = green in LW; inert in SW | ||
| + | * Pleochroism = weak to strong; light and dark green | ||
| + | * Dispersion = weak to distinct | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 22: | Line 25: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Mohs Hardness | ! scope="row"| Mohs Hardness | ||
| − | | 5. | + | | 5.5 - 6.5 |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 3.2-3.6 | + | | 3.2-3.6 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| − | | 1.66-1. | + | | 1.66-1.73 |
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Birefringence | ||
| + | | 0.024 - 0.030 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Diopside.shtml Diopside] | ||
| + | * Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016. | ||
| + | * Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 | ||
| + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "diopside" [Accessed December 4, 2001]. (tech info) | ||
| + | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diopside Diopside] (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005 and Dec 2022) | ||
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | |||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
Latest revision as of 14:23, 20 December 2022
Description
A green, calcium magnesium silicate mineral sometimes used as a Gemstone. Diopside is a Pyroxene type mineral with short, monoclinic crystals. The transparent to translucent crystals have either a square or octagonal cross section. The color of diopside crystals usually from light to dark green, but may be blue, brown, colorless or pale violet. Diopside has been found at many locations throughout Europe (Russia, Finland, Sweden, Switzerland and Italy), Canada (Ontario, Quebec) and the United States (New York, California and Maine). Powdered diopside is used as a matting agent in ceramic glazes.
Synonyms and Related Terms
calcium magnesium silicate; diopside (Fr.); diópsido (Esp., Port.); Diposid (Deut.); diopsiet (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Monoclinic system with slender square or octagonal prisms that are often twinned
- Cleavage occurs at intersecting angles of 87 and 93 degrees
- Fracture = uneven to conchoidal
- Luster = vitreous to dull
- Streak = white, gray or green
- Fluorescence = green in LW; inert in SW
- Pleochroism = weak to strong; light and dark green
- Dispersion = weak to distinct
| Composition | CaMgSi2O6 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 5.5 - 6.5 |
| Density | 3.2-3.6 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.66-1.73 |
| Birefringence | 0.024 - 0.030 |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Diopside
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "diopside" [Accessed December 4, 2001]. (tech info)
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: Diopside (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005 and Dec 2022)
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998