Difference between revisions of "Melamine resin"
(username removed) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | Any synthetic resin made with melamine and an aldehyde. The most popular melamine resin is [ | + | Any synthetic resin made with melamine and an aldehyde. The most popular melamine resin is [[melamine%20formaldehyde%20resin|melamine formaldehyde]]. Developed in 1933 by CIBA, it was widely used for molded plastic products. Butylated melamine resins are used in paints and enamels. They cure to a hard, durable glossy film that is chemically resistant. Melamine acrylic resins have been used for automotive finishes. In the late 1990s, melamine was successfully made into fibers (Basofil®). The low-cost fibers are resistant to high temperatures but have low tensile strength and are often blended with other fibers such as [[aramid%20fiber|aramids]]. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | melamine; resina de melamina (Esp.); | + | melamine; resina de melamina (Esp.); résine mélamine (Fr.); resina melaminica (It.); resina de melamilna (Port.) |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Examples: Melmac; Formica® [Formica]; amino resin Basofil® [BASF] | ||
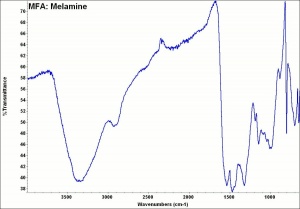
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Melamine.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Melamine.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 15: | ||
[[media:download_file_279.pdf|General Characteristics of Polymers]] | [[media:download_file_279.pdf|General Characteristics of Polymers]] | ||
| + | ==Resources and Citations== | ||
| + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 501 | ||
| − | + | * ASTM, "Standard Terminology Relating to Paint, Varnish, Lacquer and Related Products", Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Section 6, Paints, Related Coatings and Aromatics, ASTM, D16, 7-Jan, Jul-96 | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | * ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | ||
| − | * | + | * Pam Hatchfield, ''Pollutants in the Museum Environment'', Archetype Press, London, 2002 |
| − | * | + | * Thomas C. Jester (ed.), ''Twentieth-Century Building Materials'', McGraw-Hill Companies, Washington DC, 1995 |
| − | * | + | * Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', ''Engineered Plastics'', ASM International, 1988 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:14, 18 October 2022
Description
Any synthetic resin made with melamine and an aldehyde. The most popular melamine resin is melamine formaldehyde. Developed in 1933 by CIBA, it was widely used for molded plastic products. Butylated melamine resins are used in paints and enamels. They cure to a hard, durable glossy film that is chemically resistant. Melamine acrylic resins have been used for automotive finishes. In the late 1990s, melamine was successfully made into fibers (Basofil®). The low-cost fibers are resistant to high temperatures but have low tensile strength and are often blended with other fibers such as aramids.
Synonyms and Related Terms
melamine; resina de melamina (Esp.); résine mélamine (Fr.); resina melaminica (It.); resina de melamilna (Port.)
Examples: Melmac; Formica® [Formica]; amino resin Basofil® [BASF]
Comparisons
Physical Properties for Selected Thermoset Resins
General Characteristics of Polymers
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 501
- ASTM, "Standard Terminology Relating to Paint, Varnish, Lacquer and Related Products", Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Section 6, Paints, Related Coatings and Aromatics, ASTM, D16, 7-Jan, Jul-96
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Thomas C. Jester (ed.), Twentieth-Century Building Materials, McGraw-Hill Companies, Washington DC, 1995
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988