Difference between revisions of "Calcium acetate"
(username removed) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A white powder prepared by treating [ | + | A white powder prepared by treating [[acetic acid]] with [[calcium carbonate]] or [[lime]]. Calcium acetate is a water-soluble compound that has been used for aqueous and nonaqueous neutralization and alkalization of paper (AIC Book and Paper Catalog). However, during the neutralization process, calcium acetate is converted to calcium carbonate with the release of acetic acid. Any residual calcium acetate will continue to release acetic acid. Calcium acetate has also been used to reintroduce calcium ions into weathered glass (Corvaia, et. al 1996). Calcium acetate is used commercially as a mordant in dyeing and printing textiles, for liming rosin, for curing and tanning skins, and as a metallic soap. |
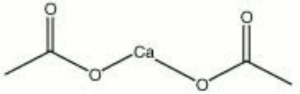
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|calcium acetate.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
calcium diacetate; lime acetate; acetate of lime; vinegar salts; gray acetate; brown acetate | calcium diacetate; lime acetate; acetate of lime; vinegar salts; gray acetate; brown acetate | ||
| − | [ | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * Combustible. | ||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AC211052500&productDescription=CALCIUM+ACETATE+HYDRATE%2C+250GR&vendorId=VN00032119&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== |
| − | Rod-shaped crystals. Soluble in water (pH = 7.6 for 0.2M solution). Slightly soluble in methanol. Insoluble in ethanol, acetone, benzene. | + | * Rod-shaped crystals. |
| + | * Soluble in water (pH = 7.6 for 0.2M solution). | ||
| + | * Slightly soluble in methanol. Insoluble in ethanol, acetone, benzene. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 22: | Line 27: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | > 160 | + | | > 160 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | about 1.5 | + | | about 1.5 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 31: | Line 36: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * C.Corvaia, I.MacLeod, C.Harley "Conservation of Glass Recovered from Shipwreck Sites" ICOM preprints, 1996 Edinburgh, vol.II p.819-825. | |
* Thomas Gregory, ''The Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942 | * Thomas Gregory, ''The Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942 | ||
Latest revision as of 14:31, 11 May 2022
Description
A white powder prepared by treating Acetic acid with Calcium carbonate or Lime. Calcium acetate is a water-soluble compound that has been used for aqueous and nonaqueous neutralization and alkalization of paper (AIC Book and Paper Catalog). However, during the neutralization process, calcium acetate is converted to calcium carbonate with the release of acetic acid. Any residual calcium acetate will continue to release acetic acid. Calcium acetate has also been used to reintroduce calcium ions into weathered glass (Corvaia, et. al 1996). Calcium acetate is used commercially as a mordant in dyeing and printing textiles, for liming rosin, for curing and tanning skins, and as a metallic soap.
Synonyms and Related Terms
calcium diacetate; lime acetate; acetate of lime; vinegar salts; gray acetate; brown acetate
Risks
- Combustible.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Rod-shaped crystals.
- Soluble in water (pH = 7.6 for 0.2M solution).
- Slightly soluble in methanol. Insoluble in ethanol, acetone, benzene.
| Composition | C4H6CaO4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 62-54-4 |
| Melting Point | > 160 C |
| Density | about 1.5 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 158.17 |
Resources and Citations
- C.Corvaia, I.MacLeod, C.Harley "Conservation of Glass Recovered from Shipwreck Sites" ICOM preprints, 1996 Edinburgh, vol.II p.819-825.
- Thomas Gregory, The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 133
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1683
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989