Difference between revisions of "Aramid fiber"
(username removed) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:017-3710.jpg|thumb|Nomex® Soft Wrap]] | [[File:017-3710.jpg|thumb|Nomex® Soft Wrap]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| + | [[File:kevlarfiberslarge.jpg|thumb|Aramid fiber]] | ||
| + | A manufactured fiber in which the fiber-forming substance is any long chain synthetic polyamide in which at least 85% of the amide linkages are directly attached to two aromatic rings (Federal Trade Commission definition). Two types of aramids, meta-aramid (e.g., [[Nomex|Nomex®]]) and para-aramid (e.g., [[Kevlar|Kevlar®]]) are made. Both types of aramid fibers are lightweight and provide extremely high strength. They also have excellent temperature, abrasion and stretch resistance. In addition, meta-aramids are soft and electrically conductive. Para-aramids are stiff, and have greater tenacity and strength than the meta-aramids. However, para-aramids are sensitive to chemicals and will degrade in the presence of acids, alkalis and bleaches. In general, aramids are used in many applications such as bulletproof vests, aerospace construction, protective clothing, high pressure hoses, tires, ropes and high strength honeycomb foams ("HRH 10"). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 10: | Line 9: | ||
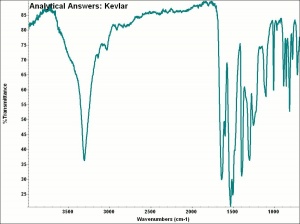
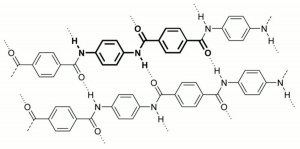
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiKEVLAR.jpg~FTIR|KevlarchemistructureF5.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiKEVLAR.jpg~FTIR|KevlarchemistructureF5.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| − | + | * Nonflammable. | |
| + | * Degrades in ultraviolet light | ||
| − | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | |
| − | + | * Resistant to most organic solvents. | |
| − | + | * Para-aramids are degraded by acids, alkalis and oxidizing agents. | |
| − | + | * Tenacity = 4.2-32.5 g/denier (dry); 3.2-18 (wet) | |
| − | + | * Elongation 3-30% (dry); 4-27% (wet) | |
| − | + | * Moisture regain = 3.5-7.0 % | |
| − | + | * Density = 1.38-1.45 g/ml | |
| − | + | * Melting Point > 410 C | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 38: | Line 30: | ||
[[media:download_file_57.pdf|Fiber Burn Tests]] | [[media:download_file_57.pdf|Fiber Burn Tests]] | ||
| − | + | == Resources and Citations == | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
* J.Gordon Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres'', Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England Comment: p.329 | * J.Gordon Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres'', Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England Comment: p.329 | ||
| Line 48: | Line 38: | ||
* Marjory L. Joseph, ''Introductory Textile Science'', Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986 | * Marjory L. Joseph, ''Introductory Textile Science'', Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aramid (Accessed Oct. 18, 2005) |
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
| Line 58: | Line 48: | ||
* Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', ''Engineered Plastics'', ASM International, 1988 | * Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', ''Engineered Plastics'', ASM International, 1988 | ||
| − | * Website | + | * Website: www.textileworld.com/categories/9905/fibers/html |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:41, 6 July 2023
Description
A manufactured fiber in which the fiber-forming substance is any long chain synthetic polyamide in which at least 85% of the amide linkages are directly attached to two aromatic rings (Federal Trade Commission definition). Two types of aramids, meta-aramid (e.g., Nomex®) and para-aramid (e.g., Kevlar®) are made. Both types of aramid fibers are lightweight and provide extremely high strength. They also have excellent temperature, abrasion and stretch resistance. In addition, meta-aramids are soft and electrically conductive. Para-aramids are stiff, and have greater tenacity and strength than the meta-aramids. However, para-aramids are sensitive to chemicals and will degrade in the presence of acids, alkalis and bleaches. In general, aramids are used in many applications such as bulletproof vests, aerospace construction, protective clothing, high pressure hoses, tires, ropes and high strength honeycomb foams ("HRH 10").
Synonyms and Related Terms
aromatic polyamide (full name); aramid fibre; Nomex® [DuPont]; Kevlar® (originally Fiber B) [DuPont]; TeijinConex® [Teijin]; Twaron® [Azko]; Technora® [Teijin]; Fenilon; Arenka®; Kermel; meta-aramid; para-aramid; Aramidfasern (Deut.); fibre aramide (Fr.); fibra de aramida (Esp.); aramide (Ned.)aromatic polyamide (full name); aramid fibre; Nomex® [DuPont]; Kevlar® (originally Fiber B) [DuPont]; TeijinConex® [Teijin]; Twaron® [Azko]; Technora® [Teijin]; Fenilon; Arenka®; Kermel; meta-aramid; para-aramid; Aramidfasern (Deut.); fibre aramide (Fr.); fibra de aramida (Esp.); aramide (Ned.)
Risks
- Nonflammable.
- Degrades in ultraviolet light
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Resistant to most organic solvents.
- Para-aramids are degraded by acids, alkalis and oxidizing agents.
- Tenacity = 4.2-32.5 g/denier (dry); 3.2-18 (wet)
- Elongation 3-30% (dry); 4-27% (wet)
- Moisture regain = 3.5-7.0 %
- Density = 1.38-1.45 g/ml
- Melting Point > 410 C
Comparisons
Properties of Synthetic Fibers
Resources and Citations
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England Comment: p.329
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985 Comment: moisture regain = 2-3%
- Marjory L. Joseph, Introductory Textile Science, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aramid (Accessed Oct. 18, 2005)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- Meredith Montague, contributed information, 1998
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988
- Website: www.textileworld.com/categories/9905/fibers/html