Difference between revisions of "Kyanite"
(username removed) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Kyaniteemr1.jpg|thumb|Kyanite]] | [[File:Kyaniteemr1.jpg|thumb|Kyanite]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:Kyanite.Gile.Mtn2.jpg|thumb|Kyanite]] | |
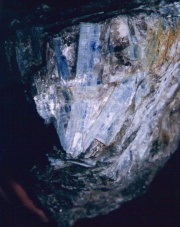
| − | A natural bluish-green aluminum silicate mineral. Kyanite has transparent, triclinic long-bladed crystals that appear fibrous or blade-like. It is a common mineral; most of the world's production is from mines in India, Kenya, Ural Mountains, Austria, Italy (Trentino), Switzerland, France and the United States (Massachusetts, Connecticut, North Carolina, Georgia, Virginia). Some clear blue kyanite crystals have been used as [ | + | A natural bluish-green aluminum silicate mineral. Kyanite has transparent, triclinic long-bladed crystals that appear fibrous or blade-like. It is a common mineral; most of the world's production is from mines in India, Kenya, Ural Mountains, Austria, Italy (Trentino), Switzerland, France and the United States (Massachusetts, Connecticut, North Carolina, Georgia, Virginia). Some clear blue kyanite crystals have been used as [[gemstone|gemstones]]. Kyanite powder, obtained from Florida beach sands, is used for glassmaking and [[ceramic|ceramics]]. Since kyanite is [[refractory material|refractory]], it is commonly used for lining furnaces. A synthetic kyanite, called Cerox ceramic, is also used for furnace parts. |
| − | + | [[File:kyanitequartzitelarge.jpg|thumb|Kyanite]] | |
| − | [[File: | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
yanite; disthene; rhoetizite; Cerox ceramic; aluminum silicate; Kyanit (Deut.); Cyanit (Deut.); cianite (It., Port.); kyaniet (Ned.) | yanite; disthene; rhoetizite; Cerox ceramic; aluminum silicate; Kyanit (Deut.); Cyanit (Deut.); cianite (It., Port.); kyaniet (Ned.) | ||
| − | + | ==Risks== | |
| − | == | + | * Kyanite Mining: [https://uwaterloo.ca/fine-arts/sites/ca.fine-arts/files/uploads/files/kyanite_35-48-100_09-25-14.pdf SDS] |
| − | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | |
| − | Triclinic system | + | [[File:Kyanite IR-ATR RRUFF R040119.png|thumb|Infrared spectrum of kyanite from [https://rruff.info/kyanite/display=default/R040119 RRUFF]]] |
| − | + | [[File:Kyanite RamanRRUFF R040119.png|thumb|Raman spectrum of kyanite from [https://rruff.info/kyanite/display=default/R040119 RRUFF]]] | |
| − | Cleavage is perfect lengthwise and good in another direction | + | * Triclinic system with columnar, fibrous or bladed crystals |
| − | + | * Luster = vitreous to pearly | |
| − | Mohs hardness is 4-5 lengthwise and 6-7 crosswise. | + | * Fracture = splintery |
| + | * Streak = white | ||
| + | * Cleavage is perfect lengthwise and good in another direction | ||
| + | * Mohs hardness is 4-5 lengthwise and 6-7 crosswise. | ||
| + | * Fluorescence = weak red under LW | ||
| + | * Pleochroism = trichroic; moderate intensity; usually colorless, dark blue and violet | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 30: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 3290 | + | | 3290 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 3.56-3.67 | + | | 3.56-3.67 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| 1.71; 1.72; 1.73 | | 1.71; 1.72; 1.73 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Birefringence | ||
| + | | 0.012 - 0.017 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | ==Resources and Citations== | |
| − | == | + | * Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016. |
| − | + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Kyanite.shtml Kyanite] | |
| − | Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Kyanite.shtml Kyanite] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 | * Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 | ||
| − | |||
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| − | |||
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "kyanite" [Accessed December 4, 2001]. | |
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "kyanite" | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyanite (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005 and Dec 2022) |
| − | |||
| − | * Wikipedia | ||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 434 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 434 | ||
| − | |||
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
| − | |||
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
Latest revision as of 11:11, 17 December 2022
Description
A natural bluish-green aluminum silicate mineral. Kyanite has transparent, triclinic long-bladed crystals that appear fibrous or blade-like. It is a common mineral; most of the world's production is from mines in India, Kenya, Ural Mountains, Austria, Italy (Trentino), Switzerland, France and the United States (Massachusetts, Connecticut, North Carolina, Georgia, Virginia). Some clear blue kyanite crystals have been used as gemstones. Kyanite powder, obtained from Florida beach sands, is used for glassmaking and ceramics. Since kyanite is refractory, it is commonly used for lining furnaces. A synthetic kyanite, called Cerox ceramic, is also used for furnace parts.
Synonyms and Related Terms
yanite; disthene; rhoetizite; Cerox ceramic; aluminum silicate; Kyanit (Deut.); Cyanit (Deut.); cianite (It., Port.); kyaniet (Ned.)
Risks
- Kyanite Mining: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties


- Triclinic system with columnar, fibrous or bladed crystals
- Luster = vitreous to pearly
- Fracture = splintery
- Streak = white
- Cleavage is perfect lengthwise and good in another direction
- Mohs hardness is 4-5 lengthwise and 6-7 crosswise.
- Fluorescence = weak red under LW
- Pleochroism = trichroic; moderate intensity; usually colorless, dark blue and violet
| Composition | Al2O3.SiO3 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 4 - 7 (directional) |
| Melting Point | 3290 C |
| Density | 3.56-3.67 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.71; 1.72; 1.73 |
| Birefringence | 0.012 - 0.017 |
Resources and Citations
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Mineralogy Database: Kyanite
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "kyanite" [Accessed December 4, 2001].
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyanite (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005 and Dec 2022)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 434
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997