Difference between revisions of "Quercetin"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A common flavonol pigment that occurs naturally in many plants, especially in [ | + | A common flavonol pigment that occurs naturally in many plants, especially in [[oak%20bark|oak bark]], [[tea%20leaves|tea leaves]], [[onion|onion]] skins, Douglas fir bark, clover blossoms, and ragweed pollen. Quercetin is yellow crystalline powder that is used medicinally and as a textile dye or colorant. It produces a bright yellow with alum and tin, a tan with chrome, and an olive green with iron. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Natural Yellow 10; CI 75670; 3.3',4',5,7-pentahydroxyflavone; quercitina (Esp.); quercetina (Port.); meletin; sophoretin; cyanidenolon 1522; ; 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-I-benzopyran-4-one | Natural Yellow 10; CI 75670; 3.3',4',5,7-pentahydroxyflavone; quercitina (Esp.); quercetina (Port.); meletin; sophoretin; cyanidenolon 1522; ; 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-I-benzopyran-4-one | ||
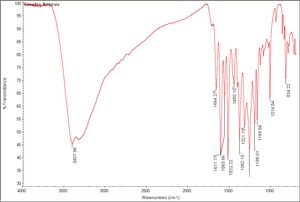
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign| | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Quercetin Dihydrate.TIF~FTIR(MFA)]]] |
| + | ==Risks== | ||
| − | == | + | * Contact may cause irritation. |
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/56284.htm MSDS] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | Soluble in ethanol, acetic acid and dilute alkali. Insoluble in water. | + | * Soluble in ethanol, acetic acid and dilute alkali. Insoluble in water. |
| − | + | * UV max (in ethanol) 258 and 375 nm. | |
| − | UV max (in ethanol) 258 and 375 nm. | + | * Crystallizes as yellow needles from alcohol. |
| − | |||
| − | Crystallizes as yellow needles from alcohol. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 315 (dec) | + | | 315 C (dec) |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
Latest revision as of 12:57, 27 September 2022
Description
A common flavonol pigment that occurs naturally in many plants, especially in Oak bark, Tea leaves, Onion skins, Douglas fir bark, clover blossoms, and ragweed pollen. Quercetin is yellow crystalline powder that is used medicinally and as a textile dye or colorant. It produces a bright yellow with alum and tin, a tan with chrome, and an olive green with iron.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Natural Yellow 10; CI 75670; 3.3',4',5,7-pentahydroxyflavone; quercitina (Esp.); quercetina (Port.); meletin; sophoretin; cyanidenolon 1522; ; 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-I-benzopyran-4-one
Risks
- Contact may cause irritation.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in ethanol, acetic acid and dilute alkali. Insoluble in water.
- UV max (in ethanol) 258 and 375 nm.
- Crystallizes as yellow needles from alcohol.
| Composition | C5H15O2(OH)5 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 117-39-5 |
| Melting Point | 315 C (dec) |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 302.23 |
Resources and Citations
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 8216
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: 'Pigment'
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 557
- John and Margaret Cannon, Dye Plants and Dyeing, Herbert Press, London, 1994
- F. Crace-Calvert, Dyeing and Calico Printing, Palmer & Howe, London, 1876
- Judith Hofenk-de Graaff, Natural Dyestuffs: Origin, Chemical Constitution, Identification, Central Research Laboratory for Objects of Art and Science, Amsterdam, 1969