Difference between revisions of "Diazinon"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
A liquid [[insecticide]] widely used to control fire ants, [[silverfish]], fleas, ticks, flies, [[moth|moths]], [[termite|termites]], and [[cockroach|cockroaches]]. Diazinon was introduced in 1952. It is an organophosphate type insecticide that works as a cholinesterase inhibitor. Diazinon is used for homes, gardens and pets, but it has harmful effects on birds, bees, and fish. | A liquid [[insecticide]] widely used to control fire ants, [[silverfish]], fleas, ticks, flies, [[moth|moths]], [[termite|termites]], and [[cockroach|cockroaches]]. Diazinon was introduced in 1952. It is an organophosphate type insecticide that works as a cholinesterase inhibitor. Diazinon is used for homes, gardens and pets, but it has harmful effects on birds, bees, and fish. | ||
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|diazinonir.jpg~FTIR|diazinonstr.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
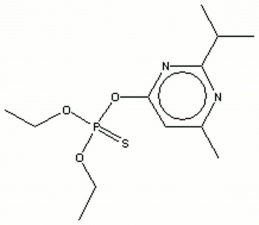
O,O-diethyl-O(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl) phosphorothioate; dimpylate, Dianon®; Diazide®; Diazol®; Neocidal®; Sarolex®; Knox-Out; Spectracide | O,O-diethyl-O(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl) phosphorothioate; dimpylate, Dianon®; Diazide®; Diazol®; Neocidal®; Sarolex®; Knox-Out; Spectracide | ||
| − | + | == Risks == | |
| − | == | + | * Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. |
| + | * May discolor organic red dyes. | ||
| + | * ECHEMI: [https://www.echemi.com/sds/diazinon-pid_Seven21915.html SDS] | ||
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
Soluble in petroleum solvents, alcohols and ketones. Slightly soluble in water. | Soluble in petroleum solvents, alcohols and ketones. Slightly soluble in water. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 26: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 1.116-1.118 | + | | 1.116-1.118 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 32: | Line 35: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ||
| − | | 83-84 | + | | 83-84 C |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Resources and Citations== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry #3043 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry #3043 | ||
| Line 55: | Line 48: | ||
* Pam Hatchfield, ''Pollutants in the Museum Environment'', Archetype Press, London, 2002 | * Pam Hatchfield, ''Pollutants in the Museum Environment'', Archetype Press, London, 2002 | ||
| − | * | + | * Conservation termlist : www.hants.org.uk/museums |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:10, 21 July 2022
Description
A liquid Insecticide widely used to control fire ants, Silverfish, fleas, ticks, flies, moths, termites, and cockroaches. Diazinon was introduced in 1952. It is an organophosphate type insecticide that works as a cholinesterase inhibitor. Diazinon is used for homes, gardens and pets, but it has harmful effects on birds, bees, and fish.
Synonyms and Related Terms
O,O-diethyl-O(2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl) phosphorothioate; dimpylate, Dianon®; Diazide®; Diazol®; Neocidal®; Sarolex®; Knox-Out; Spectracide
Risks
- Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption.
- May discolor organic red dyes.
- ECHEMI: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in petroleum solvents, alcohols and ketones. Slightly soluble in water.
| Composition | C12H21N2O3PS |
|---|---|
| CAS | 333-41-5 |
| Density | 1.116-1.118 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 304.4 |
| Refractive Index | 1.4978-1.4981 |
| Boiling Point | 83-84 C |
Resources and Citations
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry #3043
- Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, A Guide to Museum Pest Control, FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988
- J. Dawson, CCI Technical Bulletin, 'Solving Museum Insect Problems: Chemical Control' , Canadian Conservation Institute, Ottawa, No. 15
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Conservation termlist : www.hants.org.uk/museums