Difference between revisions of "Chrome orange"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
basic lead (II) chromate; Pigment Orange 21 and 45; CI 77601; phoenicochroite (mineral); anaranjado de cromo (Esp.); Chromorange (Deut.); chromorange (Fr.); portokali toy chromioy (Gr.); arancio cromo (It.); chroomoranje (Ned.); laranja de crómio (Port.); orange paste; American vermilion; plumbous chromate | basic lead (II) chromate; Pigment Orange 21 and 45; CI 77601; phoenicochroite (mineral); anaranjado de cromo (Esp.); Chromorange (Deut.); chromorange (Fr.); portokali toy chromioy (Gr.); arancio cromo (It.); chroomoranje (Ned.); laranja de crómio (Port.); orange paste; American vermilion; plumbous chromate | ||
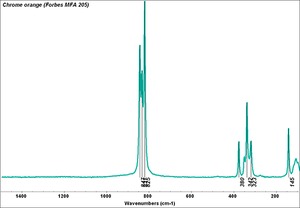
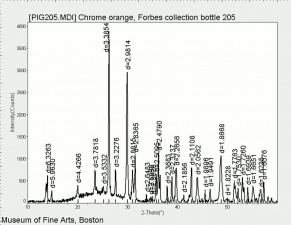
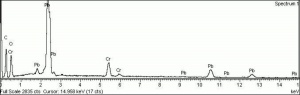
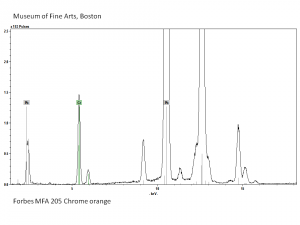
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|PIG205.jpg~XRD|f205sem.jpg~SEM|f205edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide17 FC205.PNG~XRF]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Chrome orange (Forbes MFA 205) resize.tif~Raman (MFA)|PIG205.jpg~XRD|f205sem.jpg~SEM|f205edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide17 FC205.PNG~XRF]]] |
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| − | Soluble in strong acids and alkalis. Insoluble in water. Can change to yellow in acetic acid. | + | * Toxic by inhalation or ingestion. |
| + | * Skin contact may cause irritation or ulcers. | ||
| + | * Carcinogen, teratogen, suspected mutagen. | ||
| + | * Discolored by heat and sulfur fumes | ||
| + | * Cornelissen: [https://www.cornelissen.com/media/catalog/customfield/MSDS_PGR_Chrome_Yellow_Orange.pdf SDS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Soluble in strong acids and alkalis. Insoluble in water. | ||
| + | * Can change to yellow in acetic acid. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 35: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 844 | + | | 844 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 6.3-6.7 | + | | 6.3-6.7 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 38: | Line 47: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * H. Kuhn, M.Curran, "Chrome Yellow and Other Chromate Pigments", ''Artists Pigments'', Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986. | |
* R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | ||
| Line 64: | Line 61: | ||
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5423 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5423 | ||
| − | * | + | * Web Exhibits: http://webexhibits.org/pigments/indiv/overview/crorange.html |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:22, 29 May 2022
Description
A basic lead chromate pigment that ranges in shades from orange to red. First made in 1809 by Vauquelin, basic lead chromate is formed by heating lead chromate and sodium hydroxide solution. The color of chrome red, or chrome orange can vary from a brown-yellow to a brick-red color depending on particle size and to the ratio of lead oxide to lead chromate. It is stable in light but is not widely used because of its sensitivity to sulfur gases. Most often, chrome red is used as an anticorrosive base coats for steel. See also Chrome yellow.
Synonyms and Related Terms
basic lead (II) chromate; Pigment Orange 21 and 45; CI 77601; phoenicochroite (mineral); anaranjado de cromo (Esp.); Chromorange (Deut.); chromorange (Fr.); portokali toy chromioy (Gr.); arancio cromo (It.); chroomoranje (Ned.); laranja de crómio (Port.); orange paste; American vermilion; plumbous chromate
Risks
- Toxic by inhalation or ingestion.
- Skin contact may cause irritation or ulcers.
- Carcinogen, teratogen, suspected mutagen.
- Discolored by heat and sulfur fumes
- Cornelissen: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in strong acids and alkalis. Insoluble in water.
- Can change to yellow in acetic acid.
| Composition | PbO-CrO3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7758-97-6 |
| Mohs Hardness | 2.5 |
| Melting Point | 844 C |
| Density | 6.3-6.7 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 323.2 |
| Refractive Index | 2.42; 2.7; 2.7 |
Resources and Citations
- H. Kuhn, M.Curran, "Chrome Yellow and Other Chromate Pigments", Artists Pigments, Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986.
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5423