Difference between revisions of "Lodgepole pine"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Lodgepole pine MFA.jpg|thumb|Ansel Adams<br>MFA# 2018.2389]] |
| − | + | [[File:LodgepolePinevt.jpg|thumb|Lodgepole Pine (''Pinus contorta'')]] | |
| − | (''Pinus contorta'')]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A tall, narrow pine tree (''Pinus contorta'') native to the western parts of North America. The lodgepole pine has a stiff, straight-grain wood. It is used for lumber, log cabins and telephone poles. Lodgepole pines are also used for making kraft paper, paperboard and book paper. | + | A tall, narrow pine tree (''Pinus contorta'') native to the western parts of North America. The lodgepole pine has a stiff, straight-grain wood. It is used for lumber, log cabins and telephone poles. Lodgepole pines are also used for making [[kraft paper]], [[paperboard]] and book paper. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | Pinus contorta; shore pine (Pinus contorta subsp. contorta); lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta subsp. latifolia); tamarack pine (Pinus contorta subsp. murrayana); jack pine; Küstenkiefer (Deut.); Drehkiefer (Deut.); Sosna wydmowa (Pol.); | + | ''Pinus contorta''; shore pine (''Pinus contorta'' subsp. contorta); lodgepole pine (''Pinus contorta'' subsp. latifolia); tamarack pine (''Pinus contorta'' subsp. murrayana); jack pine; Küstenkiefer (Deut.); Drehkiefer (Deut.); Sosna wydmowa (Pol.); |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:PinuscontortaMurrayavt.jpg|thumb|Tamarack pine ''Pinus contorta Murrayana'']] |
| − | + | == Risks == | |
| − | == | + | |
| + | Considered an invasive species in New Zealand. | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Grows to 30-40 m, usually tall but may be bent and twisted along the coast. Leaves=needle-like and paired (3-7 cm) Woody cones: often tightly closed; scales have spines at tip, may remain closed for years. | Grows to 30-40 m, usually tall but may be bent and twisted along the coast. Leaves=needle-like and paired (3-7 cm) Woody cones: often tightly closed; scales have spines at tip, may remain closed for years. | ||
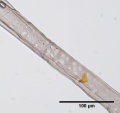
Paper fiber type: Softwood, hard pine. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified by the presence of variable-sized pinoid pits in irregular groups of 2-4 across. Compression wood is common. Dentate ray tracheids are present. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: varies with pulping and bleaching . Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.1mm, width 35-45μm. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]] and [[sulfite process|sulfite]]. | Paper fiber type: Softwood, hard pine. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified by the presence of variable-sized pinoid pits in irregular groups of 2-4 across. Compression wood is common. Dentate ray tracheids are present. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: varies with pulping and bleaching . Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.1mm, width 35-45μm. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]] and [[sulfite process|sulfite]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
| Line 27: | Line 24: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
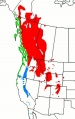
File:Pinuscontortavt.jpg|Distribution chart of lodgepole pines | File:Pinuscontortavt.jpg|Distribution chart of lodgepole pines | ||
| − | |||
File:Lodgepole pine 40x compression.jpg|Lodgepole pine paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | File:Lodgepole pine 40x compression.jpg|Lodgepole pine paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
File:Lodgepole pine 40x.jpg|Lodgepole pine paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | File:Lodgepole pine 40x.jpg|Lodgepole pine paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| Line 33: | Line 29: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
* ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | * ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | ||
| Line 43: | Line 39: | ||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lodgepole_pine (Accessed Jan. 25, 2006) |
* Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. ''Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers'' (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995. | * Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. ''Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers'' (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995. | ||
Latest revision as of 10:16, 8 October 2020
Description
A tall, narrow pine tree (Pinus contorta) native to the western parts of North America. The lodgepole pine has a stiff, straight-grain wood. It is used for lumber, log cabins and telephone poles. Lodgepole pines are also used for making Kraft paper, Paperboard and book paper.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Pinus contorta; shore pine (Pinus contorta subsp. contorta); lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta subsp. latifolia); tamarack pine (Pinus contorta subsp. murrayana); jack pine; Küstenkiefer (Deut.); Drehkiefer (Deut.); Sosna wydmowa (Pol.);
Risks
Considered an invasive species in New Zealand.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Grows to 30-40 m, usually tall but may be bent and twisted along the coast. Leaves=needle-like and paired (3-7 cm) Woody cones: often tightly closed; scales have spines at tip, may remain closed for years.
Paper fiber type: Softwood, hard pine. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified by the presence of variable-sized pinoid pits in irregular groups of 2-4 across. Compression wood is common. Dentate ray tracheids are present. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: varies with pulping and bleaching . Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.1mm, width 35-45μm. Common pulping method: kraft and sulfite.
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lodgepole_pine (Accessed Jan. 25, 2006)
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.