Difference between revisions of "Potato starch"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
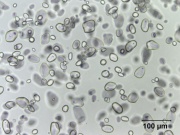
| − | [[File:3_Potato_strach_200XS.jpg|thumb|Potato starch]] | + | [[File:3_Potato_strach_200XS.jpg|thumb|Potato starch at 200x transmitted light]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
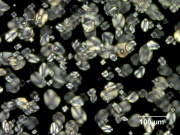
| − | + | [[File:3_Potato_strach_200XS_pol.jpg|thumb|Potato starch at 200x polarized light]] | |
| − | Polysaccharide granules obtained from the common white potato, ''Solanum tuberosum''. Potato starch is primarily used as a thickening agent for foods in Europe while [ | + | Polysaccharide granules obtained from the common white potato, ''Solanum tuberosum''. Potato starch is primarily used as a thickening agent for foods in Europe while [[cornstarch|cornstarch]] is more commonly use in the United States. When heated with water, potato starch forms a thick, gummy solution that becomes thinner with heating time. It thickens only slightly on cooling to forms a transparent gel that dries to a tough resilient film. Potato starch is used to size paper and textiles. It adds strength and tear resistance to paper. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | farina; Arogum [Morningstar-Paisley]; Arojel P | + | potato flour; farina (It.); Arogum [Morningstar-Paisley]; Arojel P |
| − | + | == Risks == | |
| − | == | ||
| − | + | * Susceptible to biodeterioration. | |
| + | * Dried films become brittle with age. | ||
| − | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | |
| − | Reacts with a iodine/potassium iodide solution to give a positive purple color | + | * Egg-shaped grains with a faint off-center dark mark (hilum). |
| − | + | * Granule size = 15-100 micrometers. | |
| − | + | * Gelatinization temperature = 59-68 C | |
| − | + | * Reacts with a iodine/potassium iodide solution to give a positive purple color | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Resources and Citations== | ||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 767 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 767 | ||
| − | |||
* Rosalie Rosso King, ''Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation'', Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985 | * Rosalie Rosso King, ''Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation'', Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985 | ||
| − | |||
* Book and Paper Group, ''Paper Conservation Catalog'', AIC, 1984, 1989 | * Book and Paper Group, ''Paper Conservation Catalog'', AIC, 1984, 1989 | ||
| − | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "cereal processing" [Accessed April 8, 2002] | |
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "cereal processing" | ||
| − | |||
* Irving Skeist, ''Handbook of Adhesives'', Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977 Comment: p. 193 | * Irving Skeist, ''Handbook of Adhesives'', Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977 Comment: p. 193 | ||
| − | + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potato_starch Potato starch] Accessed March 2025 | |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:26, 25 March 2025
Description
Polysaccharide granules obtained from the common white potato, Solanum tuberosum. Potato starch is primarily used as a thickening agent for foods in Europe while Cornstarch is more commonly use in the United States. When heated with water, potato starch forms a thick, gummy solution that becomes thinner with heating time. It thickens only slightly on cooling to forms a transparent gel that dries to a tough resilient film. Potato starch is used to size paper and textiles. It adds strength and tear resistance to paper.
Synonyms and Related Terms
potato flour; farina (It.); Arogum [Morningstar-Paisley]; Arojel P
Risks
- Susceptible to biodeterioration.
- Dried films become brittle with age.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Egg-shaped grains with a faint off-center dark mark (hilum).
- Granule size = 15-100 micrometers.
- Gelatinization temperature = 59-68 C
- Reacts with a iodine/potassium iodide solution to give a positive purple color
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 767
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "cereal processing" [Accessed April 8, 2002]
- Irving Skeist, Handbook of Adhesives, Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977 Comment: p. 193
- Wikipedia: Potato starch Accessed March 2025