Difference between revisions of "Niter"
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
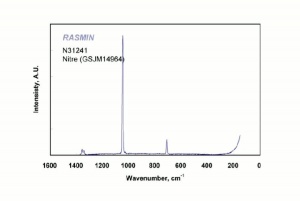
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|nitreRS.jpg~Raman]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|nitreRS.jpg~Raman]]] | ||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| − | == | + | * Can be mixed with sulfur and charcoal to form gunpowder. |
| + | * Ingestion can cause nausea and irritation | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Soluble in water (38 g in 100 g) | Soluble in water (38 g in 100 g) | ||
| Line 23: | Line 26: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 334 | + | | 334 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 2.1 | + | | 2.1 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 32: | Line 35: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ||
| − | | 400 (dec) | + | | 400 C (dec) |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* R. Mayer, ''The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques'', Viking Press, New York, 1981 | * R. Mayer, ''The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques'', Viking Press, New York, 1981 | ||
| Line 57: | Line 54: | ||
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 7815 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 7815 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potassium_nitrate (Accessed Sept. 10, 2005) |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:16, 19 October 2022
Description
Naturally occurring mineral composed of Potassium nitrate. Also known as saltpeter, niter has thin, shiny translucent crystals. It usually occurs as Efflorescence on the surface of soils in arid regions. Large quantities of niter have been found in Spain, Italy, Egypt, Arabia, India, Russia, and the United States. Niter was used during the Civil War as a component in Gunpowder. It is now used in the manufacture of Glass, matches, explosives, and fertilizers.
Synonyms and Related Terms
potassium nitrate; saltpetre; saltpeter; nitrate of potash; nitre (Br., Fr.); kaliumnitrat (Dan., Deut.); Kalisalpeter (Deut.); salpêtre (Fr.); salpêtre du Chili (Fr.); nitrato di potassio (It.); kaliumnitraat (Ned.); azotan(V) potasu (Pol.);
Risks
- Can be mixed with sulfur and charcoal to form gunpowder.
- Ingestion can cause nausea and irritation
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water (38 g in 100 g)
| Composition | KNO3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7757-79-1 |
| Melting Point | 334 C |
| Density | 2.1 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | 101.1 |
| Boiling Point | 400 C (dec) |
Resources and Citations
- R. Mayer, The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques, Viking Press, New York, 1981
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 632
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 7815
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potassium_nitrate (Accessed Sept. 10, 2005)