Difference between revisions of "Uvarovite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:Uvarovitekes.jpg|thumb|Uvarovite]] | + | [[File:Uvarovitekes.jpg|thumb|Uvarovite pendant<br>credit: Adrian Pingstone]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:pu20906uvarovite.jpg|thumb|Uvarovite]] | |
A rare, bright green [[garnet|garnet]] composed of a calcium chromium silicate. Uvarovite was discovered in 1832 and named after Count Sergei Uvarov, a Russian mineral collector. [[Gemstone|Gemstone]] quality uvarovite is mined in the Ural Mountains, Norway, Finland, Poland (Silesia), Spain, South Africa, Canada, (Quebec), and in the United States (California, Pennsylvania). | A rare, bright green [[garnet|garnet]] composed of a calcium chromium silicate. Uvarovite was discovered in 1832 and named after Count Sergei Uvarov, a Russian mineral collector. [[Gemstone|Gemstone]] quality uvarovite is mined in the Ural Mountains, Norway, Finland, Poland (Silesia), Spain, South Africa, Canada, (Quebec), and in the United States (California, Pennsylvania). | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
garnet; uvarovita (Esp.); uvarovite (Port.); Uvarovit (Deut.); uvaroviet (Ned.) | garnet; uvarovita (Esp.); uvarovite (Port.); Uvarovit (Deut.); uvaroviet (Ned.) | ||
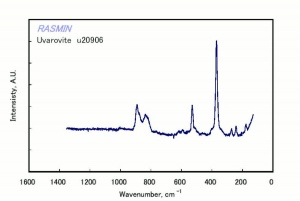
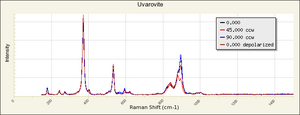
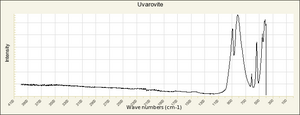
| + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|UvavoriteRS.jpg~Raman (RASMIN)|Uvarovite Raman RRUFF R061041.png~Raman (RRUFF)|Uvarovite IR-ATR RRUFF R061041.png~IR-ATR (RRUFF)]]] | ||
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
| − | + | * Cubic system with irregular closely packed euhedral crystals | |
| − | + | * Fracture = conchoidal or uneven | |
| − | + | * Luster = vitreous to resinous | |
| − | + | * Streak = white | |
| − | Fracture = conchoidal | + | * Fluorescence = not diagnostic |
| + | * Pleochroism = none | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 23: | Line 26: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 3. | + | | 3.77 - 3.81 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| − | | 1. | + | | 1.798 - 1.864 |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Uvarovite.shtml Uvarovite] | |
| − | Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Uvarovite.shtml Uvarovite] | + | * Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 354 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 354 | ||
| − | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "uvarovite" [Accessed 20 Sept. 2005]. | |
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "uvarovite" | ||
| − | |||
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| − | + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uvarovite Uvarovite] (Accessed Sept. 20, 2005 and Dec 2022) | |
| − | * Wikipedia | ||
| − | |||
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
| − | |||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:56, 19 December 2022
Description
A rare, bright green Garnet composed of a calcium chromium silicate. Uvarovite was discovered in 1832 and named after Count Sergei Uvarov, a Russian mineral collector. Gemstone quality uvarovite is mined in the Ural Mountains, Norway, Finland, Poland (Silesia), Spain, South Africa, Canada, (Quebec), and in the United States (California, Pennsylvania).
Synonyms and Related Terms
garnet; uvarovita (Esp.); uvarovite (Port.); Uvarovit (Deut.); uvaroviet (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Cubic system with irregular closely packed euhedral crystals
- Fracture = conchoidal or uneven
- Luster = vitreous to resinous
- Streak = white
- Fluorescence = not diagnostic
- Pleochroism = none
| Composition | Ca3Cr2(SiO4)3 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 6.5 - 7.5 |
| Density | 3.77 - 3.81 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.798 - 1.864 |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Uvarovite
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 354
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "uvarovite" [Accessed 20 Sept. 2005].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: Uvarovite (Accessed Sept. 20, 2005 and Dec 2022)
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998