Difference between revisions of "Persian berries LC"
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Persian_berry Persian berries] | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | + | ||
[[File:Persian-large.jpg|thumb|Persia berry dyed wool sample, photo from http://www.renaissancedyeing.com]] | [[File:Persian-large.jpg|thumb|Persia berry dyed wool sample, photo from http://www.renaissancedyeing.com]] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
== Summary of results == | == Summary of results == | ||
| − | + | ||
== Sample preparation == | == Sample preparation == | ||
| − | + | Persian berry sample (~0.1g) from Iran was extracted with 1 mL methanol:H2O (v:v=1:1). Then the upper 30 μl of solution was removed for HPLC-DAD-MS analysis (20 μl was injected). | |
== Analytical instrumentation and procedures == | == Analytical instrumentation and procedures == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
HPLC-DAD | HPLC-DAD | ||
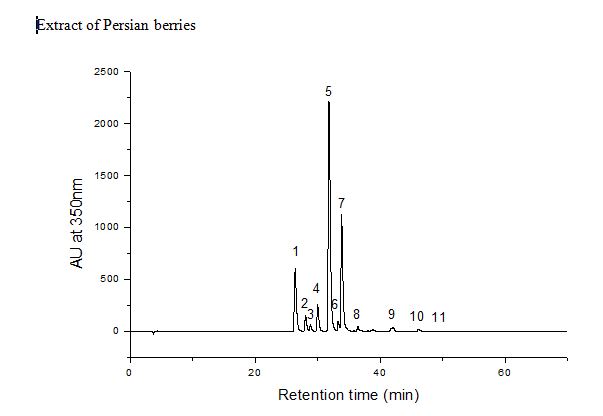
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Persian berries LC.JPG|center|frame|Extract of Persian berries in Methanol:water=1:1(v:v), By Xian Zhang Absorbance at 350nm (mAU)]] |
| − | |||
== Result == | == Result == | ||
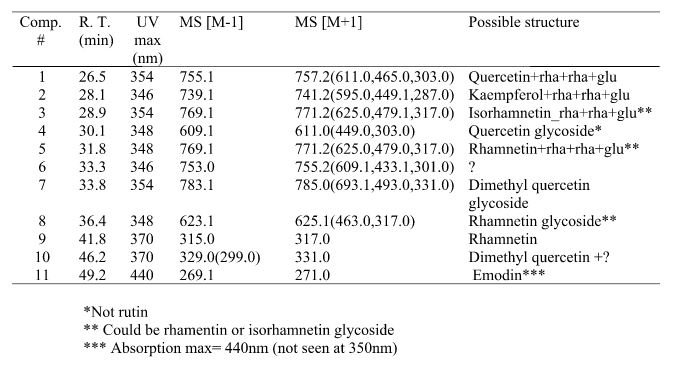
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Persian berries result.JPG|center|frame|compounds identified]] |
== Identified compounds == | == Identified compounds == | ||
| − | [[[ | + | [[[|Rutin.JPG~Rutin UV-Vis|isoUV.jpg~Quercetin UV-Vis]]] |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Latest revision as of 08:58, 20 November 2017
Description
Synonyms and Related Terms

Summary of results
Sample preparation
Persian berry sample (~0.1g) from Iran was extracted with 1 mL methanol:H2O (v:v=1:1). Then the upper 30 μl of solution was removed for HPLC-DAD-MS analysis (20 μl was injected).
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
HPLC-DAD-MS analysis was performed with an Agilent 1100 liquid chromatography system consisting of an automatic injector, a gradient pump, a HP series 1100 DAD, and an Agilent series 1100 VL on-line atmospheric pressure ionization electrospray ionization mass spectrometer. Separations were done on a Vydac 214TP52 analytical column (2.1 mm diameterX250 mm; 5-ím particle size). The column was eluted at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min with a tertiary gradient of water (A),acetonitrile (B), and 1% (v/v) aqueous formic acid (C) with the following elution program: 0 min, 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; 0-55 min, a linear gradient to 35% A, 60% B, 5% C; 55-60 min, a linear gradient elution to 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 60-62 min, isocratic elution at 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 62-70 min gradient elution to 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; and reequilibration with the latter solvent for 15 min. The mass spectrometer was run both in the negative and positive ion mode.
Chromatograms
HPLC-DAD
Result
Identified compounds
[[[|Rutin.JPG~Rutin UV-Vis|isoUV.jpg~Quercetin UV-Vis]]]
| Compound | RT (min.) | MW | UV/vis | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rutin | 27.0 | 610 | 278,352 | Comments here |
| quercetin | 34.6 | 302 | 280,395,370 | |
| kaempferol | 39.0 | 286 | 280,395,368 | |
| isorhamnetin | 39.0 | 316 | 280,395,368 |
References
- Zhang, X., and Laursen, R. A., Development of Mild Extraction Methods for the Analysis of Natural Dyes in Textiles of Historical Interest Using LC-Diode Array Detector-MS. Analytical Chemistry 77, 2022-2025 (2005).
- Zhang, X., Corrigan, K., MacLaren, B., Leveque, M., and Laursen, R. A., Characterization of Yellow Dyes in Nineteenth Century Chinese Textiles. Studies in Conservation 52, 211-220 (2007).