Difference between revisions of "Desert Poplar (Populus pruinosa) LC"
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[|thumb|Desert Polar tree (Populus pruinosa)]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | Desert Poplar, 灰胡杨, (''Populus pruinosa'')is a medium-sized deciduous tree. The tree grows up to 10 | + | Desert Poplar, 灰胡杨, (''Populus pruinosa'')is a medium-sized deciduous tree. The tree grows up to 10 to 20 m tall. The bark has grayish yellow color. It naturally grows in Central and Southwestern Asia. [1] |
== Historical importance == | == Historical importance == | ||
| + | Populus pruinosa might be the dyeing source of yellow colorants from archaeological samples excavated from Xinjiang. | ||
| + | |||
| + | examples: | ||
| Line 13: | Line 16: | ||
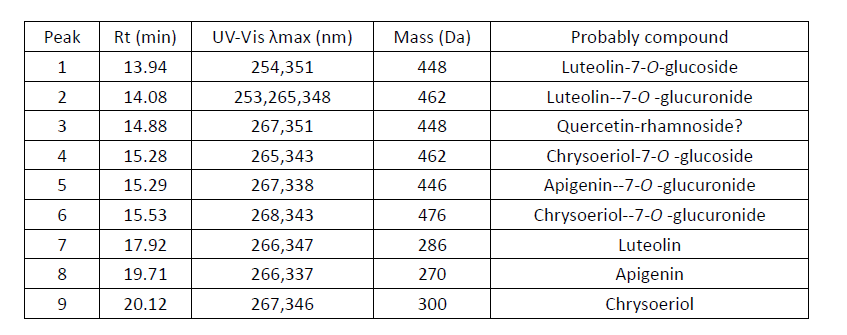
Multiple flavonoids, luteolin, apigenin, chrysoeriol and their glycosides were identified from desert poplar dyed wool samples. | Multiple flavonoids, luteolin, apigenin, chrysoeriol and their glycosides were identified from desert poplar dyed wool samples. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
== Analytical instrumentation and procedures == | == Analytical instrumentation and procedures == | ||
| + | The dye was extracted from a thread (0.2-1mg) of the dyed fiber in a solution of pyridine/water/1.0M oxalic acid as described by Mouri and Laursen [2]. The solution was evaporated to dryness under a nitrogen flow, and redissolved in 50 μL MeOH/H2O (1/1); subsequently, 20 μL of dye solution was injected onto HPLC column. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An extract was analyzed on an HPLC-PDA-MS system consisting of a Shimadzu LC-20A high performance liquid chromatography, a Shimadzu SPD-M20A photodiode array detector and a Thermo LTQ XL ion trap mass spectrometer. The separation was performed on a Shim-pack XR-ODS column (3.0 mm × 75 mm, 2.2-μm particle size) and a Phenomenex Luna C18 column (2.0 mm × 150 mm, 3-μm particle size). Columns were eluted with acetonitrile-water gradients containing 0.1% formic acid at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. | ||
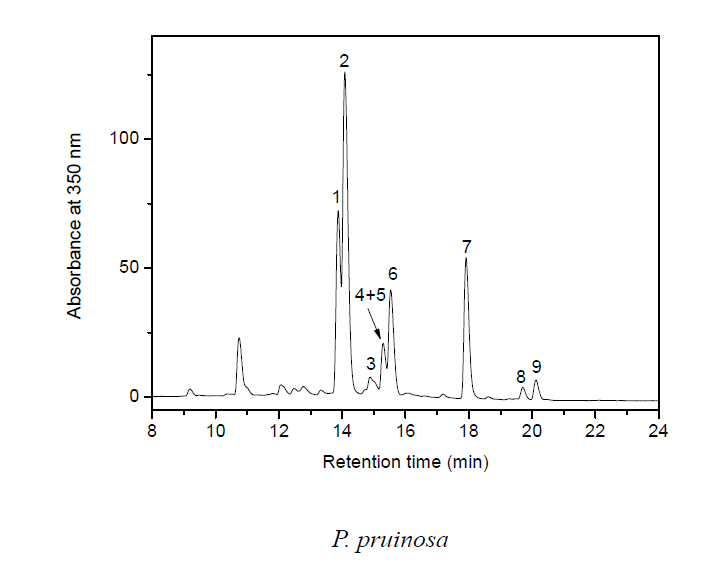
== Chromatograms == | == Chromatograms == | ||
| + | [[File:P populus LC.PNG|center|frame|Extract of P. Pruinosa dyed textile, Absorbance at 350nm (mAU) by Jian Liu, China National Silk Museum]] | ||
| + | == Compounds identified == | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:P populus compounds.PNG|center|frame|Compounds identified, By Jian Liu, China National Silk Museum ]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Identified compounds == | == Identified compounds == | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
|- | |- | ||
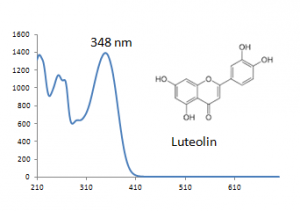
| Luteolin | | Luteolin | ||
| − | | | + | | 17.9 |
| 286 | | 286 | ||
| 348 | | 348 | ||
|- | |- | ||
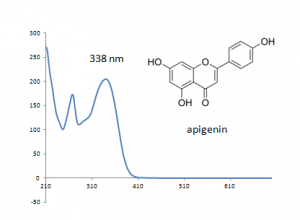
| Apigenin | | Apigenin | ||
| − | | | + | | 19.7 |
| 270 | | 270 | ||
| 338 | | 338 | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
[1] Flora of China, efloras.org ''Populus pruinosa'' http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200005695 | [1] Flora of China, efloras.org ''Populus pruinosa'' http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200005695 | ||
| − | [2] | + | |
| − | + | [2] Mouri C, Laursen R. Identification and partial characterization of C-glycosylfalvone markers in Asian plant dyes using liquid chromatogrphy tandem mass spectrometery. Journal of Chromatography A 2011; 1218: 7325-30. | |
| + | |||
[[Category:Dye Analysis]] | [[Category:Dye Analysis]] | ||
[[Category:Reference Materials]] | [[Category:Reference Materials]] | ||
[[Category:Natural Dyes]] | [[Category:Natural Dyes]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:06, 6 September 2017
[[|thumb|Desert Polar tree (Populus pruinosa)]]
Description
Desert Poplar, 灰胡杨, (Populus pruinosa)is a medium-sized deciduous tree. The tree grows up to 10 to 20 m tall. The bark has grayish yellow color. It naturally grows in Central and Southwestern Asia. [1]
Historical importance
Populus pruinosa might be the dyeing source of yellow colorants from archaeological samples excavated from Xinjiang.
examples:
Summary of results
Multiple flavonoids, luteolin, apigenin, chrysoeriol and their glycosides were identified from desert poplar dyed wool samples.
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
The dye was extracted from a thread (0.2-1mg) of the dyed fiber in a solution of pyridine/water/1.0M oxalic acid as described by Mouri and Laursen [2]. The solution was evaporated to dryness under a nitrogen flow, and redissolved in 50 μL MeOH/H2O (1/1); subsequently, 20 μL of dye solution was injected onto HPLC column.
An extract was analyzed on an HPLC-PDA-MS system consisting of a Shimadzu LC-20A high performance liquid chromatography, a Shimadzu SPD-M20A photodiode array detector and a Thermo LTQ XL ion trap mass spectrometer. The separation was performed on a Shim-pack XR-ODS column (3.0 mm × 75 mm, 2.2-μm particle size) and a Phenomenex Luna C18 column (2.0 mm × 150 mm, 3-μm particle size). Columns were eluted with acetonitrile-water gradients containing 0.1% formic acid at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min.
Chromatograms
Compounds identified
Identified compounds
| Compound | RT (min.) | MW | UV/vis | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luteolin | 17.9 | 286 | 348 | |
| Apigenin | 19.7 | 270 | 338 |
References
[1] Flora of China, efloras.org Populus pruinosa http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200005695
[2] Mouri C, Laursen R. Identification and partial characterization of C-glycosylfalvone markers in Asian plant dyes using liquid chromatogrphy tandem mass spectrometery. Journal of Chromatography A 2011; 1218: 7325-30.