Difference between revisions of "Lazulite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
A minor blue-green color gemstone composed of iron aluminum phosphate. Although its name has caused some confusion, it has no connection with [[lazurite]], the main ingredient in [[lapis lazuli]]. Lazulite is a translucent stone that has been found in Switzerland (Zermatt), Austria, Sweden, Malagasy Republic, Brazil (Minas Gerais), Canada (Yukon), and the U.S.(California, Georgia). It was used for inlays on an amulet from the Oxxus Treasure (Ogden 1982). | A minor blue-green color gemstone composed of iron aluminum phosphate. Although its name has caused some confusion, it has no connection with [[lazurite]], the main ingredient in [[lapis lazuli]]. Lazulite is a translucent stone that has been found in Switzerland (Zermatt), Austria, Sweden, Malagasy Republic, Brazil (Minas Gerais), Canada (Yukon), and the U.S.(California, Georgia). It was used for inlays on an amulet from the Oxxus Treasure (Ogden 1982). | ||
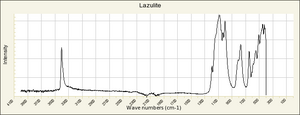
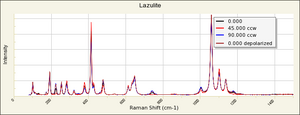
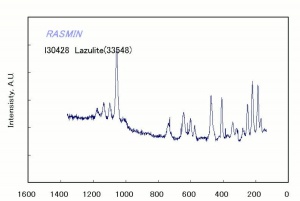
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Lazulite IR-ATR RRUFF R050110.png~IR-ATR (RRUFF)|Lazulite Raman RRUFF R050110.png~Raman (RRUFF)|lazuliteRS.jpg~Raman (RASMIN)]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | |||
Lazulit (Deut.) | Lazulit (Deut.) | ||
| − | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | Monoclinic system with bipyramidal crystals or grains | + | * Monoclinic system with bipyramidal crystals or grains |
| + | * Cleavage = poor to good in one direction | ||
| + | * Fracture = uneven, splintery | ||
| + | * Luster = vitreous to dull | ||
| + | * Streak = white | ||
| + | * Fluorescence = inert | ||
| + | * Pleochroism = strong; dark violet blue and colorless to light blue | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 20: | Line 23: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Mohs Hardness | ! scope="row"| Mohs Hardness | ||
| − | | 5. | + | | 5.5 - 6.0 |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 3.0-3.4 | + | | 3.0-3.4 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| 1.60; 1.63; 1.64 | | 1.60; 1.63; 1.64 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Birefringence | ||
| + | | 0.031 - 0.037 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[media:download_file_469.pdf|Properties of Common Gemstones]] | [[media:download_file_469.pdf|Properties of Common Gemstones]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | + | * Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016. | |
| + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Lazulite.shtml Lazulite] | ||
* Thomas Gregory, ''The Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942 | * Thomas Gregory, ''The Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942 | ||
| − | |||
* Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | * Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | ||
| − | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "lazulite." Accessed 7 Apr. 2005 . | |
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "lazulite." | ||
| − | |||
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| − | + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lazulite Lazulite] (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005 and Dec 2022) | |
| − | * Wikipedia | ||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:56, 17 December 2022
Description
A minor blue-green color gemstone composed of iron aluminum phosphate. Although its name has caused some confusion, it has no connection with Lazurite, the main ingredient in Lapis lazuli. Lazulite is a translucent stone that has been found in Switzerland (Zermatt), Austria, Sweden, Malagasy Republic, Brazil (Minas Gerais), Canada (Yukon), and the U.S.(California, Georgia). It was used for inlays on an amulet from the Oxxus Treasure (Ogden 1982).
Synonyms and Related Terms
Lazulit (Deut.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Monoclinic system with bipyramidal crystals or grains
- Cleavage = poor to good in one direction
- Fracture = uneven, splintery
- Luster = vitreous to dull
- Streak = white
- Fluorescence = inert
- Pleochroism = strong; dark violet blue and colorless to light blue
| Composition | MgAl2(OH)2(PO4)2 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 5.5 - 6.0 |
| Density | 3.0-3.4 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.60; 1.63; 1.64 |
| Birefringence | 0.031 - 0.037 |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Gemstones
Resources and Citations
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Mineralogy Database: Lazulite
- Thomas Gregory, The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "lazulite." Accessed 7 Apr. 2005 .
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: Lazulite (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005 and Dec 2022)