Difference between revisions of "Paraffin wax"
(→Risks) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Paraffinwax.jpg|thumb|Paraffin wax]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:61-79_Paraffin.Wax_canvas.jpg|thumb|Paraffin Wax on canvas (visible light left; UV light right)]] | |
A white, translucent odorless hydrocarbon wax that is chemically inert and odorless. Paraffin was first produced commercially in 1867 as a refined petroleum product composed of a mixture of saturated straight chain hydrocarbons (C22-C36). Production consists of separation by distillation followed by chemical treatment and decolorization. Synthetic paraffin wax made from coal products was introduced after World War II. The snow-white synthetic paraffin is harder and purer than petroleum-based paraffin waxes. Paraffin is used to make candles, wax paper, leather dressing, inks, lubricants, cosmetics, and sealing materials. The wax is also used for heavy-duty floor wax, waterproofing textiles and paper, tanning leather, as rust preventives, and for masonry and concrete treatment. [[Microcrystalline%20wax|Microcrystalline wax]] is a special refined grade of paraffin wax. | A white, translucent odorless hydrocarbon wax that is chemically inert and odorless. Paraffin was first produced commercially in 1867 as a refined petroleum product composed of a mixture of saturated straight chain hydrocarbons (C22-C36). Production consists of separation by distillation followed by chemical treatment and decolorization. Synthetic paraffin wax made from coal products was introduced after World War II. The snow-white synthetic paraffin is harder and purer than petroleum-based paraffin waxes. Paraffin is used to make candles, wax paper, leather dressing, inks, lubricants, cosmetics, and sealing materials. The wax is also used for heavy-duty floor wax, waterproofing textiles and paper, tanning leather, as rust preventives, and for masonry and concrete treatment. [[Microcrystalline%20wax|Microcrystalline wax]] is a special refined grade of paraffin wax. | ||
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Paraffin (Deut.); alcano (Esp.); paraffine (Fr., Ned.); parafina (Pol.); cera de parafina (Esp.); paraffina (It); microcrystalline wax; paraffin scale | Paraffin (Deut.); alcano (Esp.); paraffine (Fr., Ned.); parafina (Pol.); cera de parafina (Esp.); paraffina (It); microcrystalline wax; paraffin scale | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
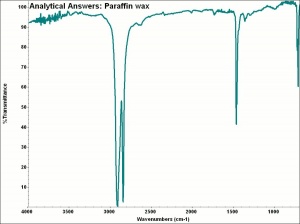
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiPARAFFIN.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiPARAFFIN.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
== Risks == | == Risks == | ||
| − | Combustible. Flash point = 204C (399F). | + | * Combustible. Flash point = 204C (399F). |
| − | + | * May contain carcinogens. | |
| − | May contain carcinogens. | + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/shop/msdsproxy?productName=AC416770020&productDescription=PARAFFIN SDS] |
| − | |||
| − | ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/shop/msdsproxy?productName=AC416770020&productDescription=PARAFFIN SDS] | ||
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | Soluble in benzene, ligroin, carbon disulfide, olive oil. | + | * Soluble in benzene, ligroin, carbon disulfide, olive oil. |
| − | + | * Insoluble in water and acids. | |
| − | Insoluble in water and acids. | + | * Acid value= 0 |
| − | + | * Iodine value=0 | |
| − | Acid value= 0 | + | * Saponification value = 0 |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 37: | Line 32: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 47-75 | + | | 47-75 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 0.880-0.925 | + | | 0.880-0.925 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| Line 50: | Line 45: | ||
[[media:download_file_29.pdf|Properties of Natural Waxes]] | [[media:download_file_29.pdf|Properties of Natural Waxes]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: mp=50-57 C | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: mp=50-57 C | ||
Latest revision as of 10:01, 26 July 2022
Description
A white, translucent odorless hydrocarbon wax that is chemically inert and odorless. Paraffin was first produced commercially in 1867 as a refined petroleum product composed of a mixture of saturated straight chain hydrocarbons (C22-C36). Production consists of separation by distillation followed by chemical treatment and decolorization. Synthetic paraffin wax made from coal products was introduced after World War II. The snow-white synthetic paraffin is harder and purer than petroleum-based paraffin waxes. Paraffin is used to make candles, wax paper, leather dressing, inks, lubricants, cosmetics, and sealing materials. The wax is also used for heavy-duty floor wax, waterproofing textiles and paper, tanning leather, as rust preventives, and for masonry and concrete treatment. Microcrystalline wax is a special refined grade of paraffin wax.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Paraffin (Deut.); alcano (Esp.); paraffine (Fr., Ned.); parafina (Pol.); cera de parafina (Esp.); paraffina (It); microcrystalline wax; paraffin scale
Risks
- Combustible. Flash point = 204C (399F).
- May contain carcinogens.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in benzene, ligroin, carbon disulfide, olive oil.
- Insoluble in water and acids.
- Acid value= 0
- Iodine value=0
- Saponification value = 0
| Composition | CnH2n+2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 8002-74-2 |
| Melting Point | 47-75 C |
| Density | 0.880-0.925 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.442-1.448 |
Comparisons
Resources and Citations
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: mp=50-57 C
- B. Gascoigne, How to Identify Prints, Thames & Hudson, London, 2004
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 581; for refined wax-melting point = 55-58C and specific gravity = 0.903
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 Comment: mp=47-65 C
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) Comment: mp=50-60 C
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 Comment: mp=50-75 C
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- George Savage, Art and Antique Restorer's Handbook, Rockliff Publishing Corp, London, 1954
- John S. Mills, Raymond White, The Organic Chemistry of Museum Objects, Butterworth Heineman, London, 2nd ed., 1994 Comment: mp=52-57 C
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraffin (Accessed Feb. 10, 2006) melting point range 47-65C
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Paraffin Wax." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2004. Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. 14 Apr. 2004 .
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=0.896-0.925; ref. index=1.442-1.448; melting point = 49-63; acid value= 0; iodine value=0, saponification value = 0
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000