Difference between revisions of "Supercritical fluid"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
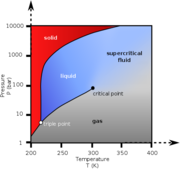
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Carbon_dioxide_pressure-temperature_phase.png|thumb|Phase diagram for carbon dioxide]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
! rowspan="2" | Solvent !! Molecular mass !! Critical temperature !! Critical pressure !! Critical density | ! rowspan="2" | Solvent !! Molecular mass !! Critical temperature !! Critical pressure !! Critical density | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! g/mol !! | + | ! g/mol !! K !! Pascal (atm) !! g/cm<sup>3</sup> |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Carbon dioxide]] (CO<sub>2</sub>) | | [[Carbon dioxide]] (CO<sub>2</sub>) | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
* Sung Mo Kang, Achim Unger, J.J. Morrell, 'The Effect of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Color Retention and Pesticide Reduction of Wooden Artifacts' ''JAIC'' 43(2) 151-160, 2004. | * Sung Mo Kang, Achim Unger, J.J. Morrell, 'The Effect of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Color Retention and Pesticide Reduction of Wooden Artifacts' ''JAIC'' 43(2) 151-160, 2004. | ||
| − | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supercritical_fluid ( | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supercritical_fluid (June 2020) |
| − | * Robert C. Reid | + | * Robert C. Reid ''The Properties of Gases and Liquids'', McGraw-Hill, 1987. |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:52, 14 June 2020
Description
A material compressed and heated to a point above its thermodynamic critical point. Supercritical fluids (SCF) have the unique ability to penetrate materials like a gas while also dissolving materials like a liquid. Carbon dioxide and water are the most commonly used supercritical fluids. A temperatures and pressures above the thermodynamic critical point, a material's liquid phase and the gas phase will have equal densities and are indistinguishable.
Synonyms and Related Terms
SCF
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Solvent | Molecular mass | Critical temperature | Critical pressure | Critical density |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/mol | K | Pascal (atm) | g/cm3 | |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | 44.01 | 304.1 | 7.38 (72.8) | 0.469 |
| Water (H2O)† | 18.015 | 647.096 | 22.064 (217.755) | 0.322 |
| Methane (CH4) | 16.04 | 190.4 | 4.60 (45.4) | 0.162 |
| Ethane (C2H6) | 30.07 | 305.3 | 4.87 (48.1) | 0.203 |
| Propane (C3H8) | 44.09 | 369.8 | 4.25 (41.9) | 0.217 |
| Ethylene (C2H4) | 28.05 | 282.4 | 5.04 (49.7) | 0.215 |
| Propylene (C3H6) | 42.08 | 364.9 | 4.60 (45.4) | 0.232 |
| Methanol (CH3OH) | 32.04 | 512.6 | 8.09 (79.8) | 0.272 |
| Ethanol (C2H5OH) | 46.07 | 513.9 | 6.14 (60.6) | 0.276 |
| Acetone (C3H6O) | 58.08 | 508.1 | 4.70 (46.4) | 0.278 |
| Nitrous oxide (N2O) | 44.013 | 306.57 | 7.35 (72.5) | 0.452 |
Resources and Citations
- Sung Mo Kang, Achim Unger, J.J. Morrell, 'The Effect of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Color Retention and Pesticide Reduction of Wooden Artifacts' JAIC 43(2) 151-160, 2004.
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supercritical_fluid (June 2020)
- Robert C. Reid The Properties of Gases and Liquids, McGraw-Hill, 1987.