Difference between revisions of "Lead chromate"
(→Risks) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Lead.chromate_det.jpg|thumb|Lead chromate]] | [[File:Lead.chromate_det.jpg|thumb|Lead chromate]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:Cryellow C100x.jpg|thumb|Chromium yellow]] | |
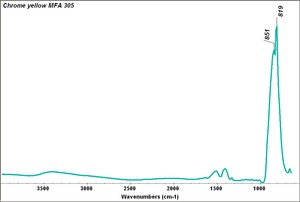
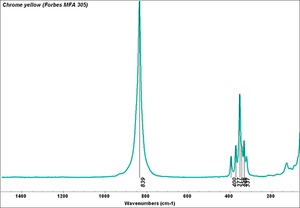
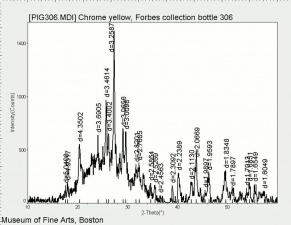
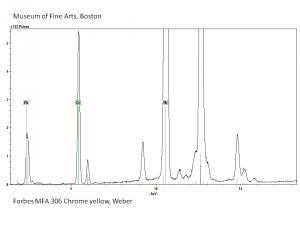
An important commercial yellow pigment called [[chrome yellow]]. Lead chromate can range in shade from lemon yellow to orange depending on its particle size and hydration state. Chrome yellow, which came on the market in early 1800s, is fairly permanent to light, but has been known to darken on aging or with exposure to [[hydrogen sulfide]]. Chrome yellow is used in industrial paint, some artists paint and ceramic glazes. | An important commercial yellow pigment called [[chrome yellow]]. Lead chromate can range in shade from lemon yellow to orange depending on its particle size and hydration state. Chrome yellow, which came on the market in early 1800s, is fairly permanent to light, but has been known to darken on aging or with exposure to [[hydrogen sulfide]]. Chrome yellow is used in industrial paint, some artists paint and ceramic glazes. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
==Risks == | ==Risks == | ||
| − | Human carcinogen, teratogen and suspected mutagen. Skin contact may cause allergies. Ingestion may cause fatal chromium/lead poisoning. Chronic inhalation may cause lung cancer and respiratory irritation. | + | * Human carcinogen, teratogen and suspected mutagen. |
| − | + | * Skin contact may cause allergies. | |
| − | ThermoFisher: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/12580.htm MSDS] | + | * Ingestion may cause fatal chromium/lead poisoning. |
| + | * Chronic inhalation may cause lung cancer and respiratory irritation. | ||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/12580.htm MSDS] | ||
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 844 | + | | 844 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 5.96-6.3 | + | | 5.96-6.3 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 41: | Line 43: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* H. Kuhn, M.Curran, "Chrome Yellow and Other Chromate Pigments", ''Artists Pigments, Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986. | * H. Kuhn, M.Curran, "Chrome Yellow and Other Chromate Pigments", ''Artists Pigments, Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986. | ||
Latest revision as of 09:25, 16 September 2022
Description
An important commercial yellow pigment called Chrome yellow. Lead chromate can range in shade from lemon yellow to orange depending on its particle size and hydration state. Chrome yellow, which came on the market in early 1800s, is fairly permanent to light, but has been known to darken on aging or with exposure to Hydrogen sulfide. Chrome yellow is used in industrial paint, some artists paint and ceramic glazes.
Synonyms and Related Terms
chrome yellow; Pigment Yellow 34; CI 77600; chromate de plomb (Fr.); cromato de plomo (Esp.); Chromgelb (Deut.); chromikos molybdos (Gr.); kitrino toy chromioy (Gr.); gialli di cromo (It.); loodchromaat (Ned.); cromato de chumbo (Port.); lead chrome yellow; chrome red; chrome orange; Paris yellow; king's yellow; Cologne yellow; Leipzig yellow
Risks
- Human carcinogen, teratogen and suspected mutagen.
- Skin contact may cause allergies.
- Ingestion may cause fatal chromium/lead poisoning.
- Chronic inhalation may cause lung cancer and respiratory irritation.
- ThermoFisher: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in strong acids and alkalis. Insoluble in water.
| Composition | PbCrO4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7758-97-6 |
| Melting Point | 844 C |
| Density | 5.96-6.3 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 323.19 |
| Refractive Index | 2.31; 2.49 |
Resources and Citations
- H. Kuhn, M.Curran, "Chrome Yellow and Other Chromate Pigments", Artists Pigments, Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986.
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: density 5.96 and ref. index 2.31; 2.49
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5422
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: "Pigments"
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000