Difference between revisions of "Adipic acid"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A white crystalline, solid that occurs naturally in beet juice. Adipic acid is prepared synthetically from cyclohexanol. It is primarily used in the production of [[nylon%20resin|Nylon]] and [[polyurethane|polyurethane]] foams. Adipic acid is also used as a [[plasticizer|plasticizer]], [[lubricant|lubricant]], and a food additive in baking powder (in place of [[cream%20of%20tartar|cream of tartar]]) and in beverages (in place of [[citric%20acid|citric acid]]). It is not [[hygroscopic|hygroscopic]]. Prior to 1940, adipic acid was also used for bronzing metals, preparing photographic paper, textile dyeing, and as a component in synthetic wax sizes mixed with [[glycerol|glycerol]], [[stearic%20acid|stearic acid]], and [[palmitic%20acid|palmitic acid]]. | + | A white crystalline, solid that occurs naturally in beet juice. Adipic acid is prepared synthetically from cyclohexanol. It is primarily used in the production of [[nylon%20resin|Nylon]] and [[polyurethane|polyurethane]] foams. Adipic acid is also used as a [[plasticizer|plasticizer]], [[lubricant|lubricant]], and a food additive in baking powder (in place of [[cream%20of%20tartar|cream of tartar]]) and in beverages (in place of [[citric%20acid|citric acid]]). It is not [[hygroscopic|hygroscopic]]. Prior to 1940, adipic acid was also used for bronzing metals, preparing photographic paper, textile dyeing, and as a component in synthetic wax sizes mixed with [[glycerol|glycerol]], [[stearic%20acid|stearic acid]], and [[palmitic%20acid|palmitic acid]]. Adipic acid may evolve from degraded polyurethane ester-type foams (Tétreault 2017). |
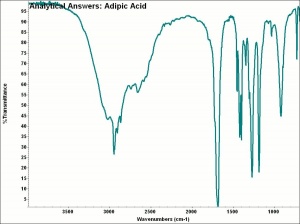
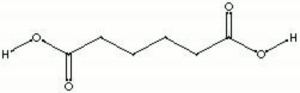
| + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiADIPIC.jpg~FTIR|adipic acid.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
hexanedioic acid; 1,4-butanedicarboxylic acid; adipinic acid' Adipinsäure (Deut.); acide adipique (Fr.); acide 1,6-hexanedioïque (Fr.); | hexanedioic acid; 1,4-butanedicarboxylic acid; adipinic acid' Adipinsäure (Deut.); acide adipique (Fr.); acide 1,6-hexanedioïque (Fr.); | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Risks== | ==Risks== | ||
| − | + | * Can cause corrosion in copper, zinc and bronze | |
| − | Fisher Scientific: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=S25124&productDescription=ADIPIC+ACID+POWDER+500G&vendorId=VN00115888&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=S25124&productDescription=ADIPIC+ACID+POWDER+500G&vendorId=VN00115888&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] |
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | Soluble in methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, acetone. Slightly soluble in water, cyclohexane. Insoluble in benzene, ligroin. | + | * Soluble in methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, acetone. Slightly soluble in water, cyclohexane. Insoluble in benzene, ligroin. |
| − | + | * pH of a saturated solution is 2.7 | |
| − | pH of a saturated solution is 2.7 | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 40: | Line 38: | ||
== Resources and Citations == | == Resources and Citations == | ||
| + | * Jean Tétreault, 'Products used in Preventive Conservation' Technical Bulletin #2, CCI, 2017. [https://www.canada.ca/en/conservation-institute/services/conservation-preservation-publications/technical-bulletins/products-used-preventive-conservation.html#a2c1 Link] | ||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 17 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 17 | ||
Latest revision as of 11:39, 20 November 2022
Description
A white crystalline, solid that occurs naturally in beet juice. Adipic acid is prepared synthetically from cyclohexanol. It is primarily used in the production of Nylon and Polyurethane foams. Adipic acid is also used as a Plasticizer, Lubricant, and a food additive in baking powder (in place of Cream of tartar) and in beverages (in place of Citric acid). It is not Hygroscopic. Prior to 1940, adipic acid was also used for bronzing metals, preparing photographic paper, textile dyeing, and as a component in synthetic wax sizes mixed with Glycerol, Stearic acid, and Palmitic acid. Adipic acid may evolve from degraded polyurethane ester-type foams (Tétreault 2017).
Synonyms and Related Terms
hexanedioic acid; 1,4-butanedicarboxylic acid; adipinic acid' Adipinsäure (Deut.); acide adipique (Fr.); acide 1,6-hexanedioïque (Fr.);
Risks
- Can cause corrosion in copper, zinc and bronze
- Fisher Scientific: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, acetone. Slightly soluble in water, cyclohexane. Insoluble in benzene, ligroin.
- pH of a saturated solution is 2.7
| Composition | COOH(CH2)4COOH |
|---|---|
| CAS | 124-04-9 |
| Melting Point | 152 C |
| Density | 1.360 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 146.14 |
| Boiling Point | 337.5 C |
Resources and Citations
- Jean Tétreault, 'Products used in Preventive Conservation' Technical Bulletin #2, CCI, 2017. Link
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 17
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry # 161