Difference between revisions of "Halite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
A mineral composed of [[sodium chloride]] that naturally occurs as colorless, cubic crystals. Halite is found in dry lakebeds, in underground salt deposits and near the ocean. Large deposits occur in Germany, Austria, Russia, France (Dax), India (Punjab), Canada (Ontario), and the U.S. (New York, Michigan, Kansas, California). It is often mined then ground for use as common table salt. Large, unground crystals are sold as rock salt. Rock salt is used to melt ice, as a food preservative, and for the production of soda ash by the glass industry. | A mineral composed of [[sodium chloride]] that naturally occurs as colorless, cubic crystals. Halite is found in dry lakebeds, in underground salt deposits and near the ocean. Large deposits occur in Germany, Austria, Russia, France (Dax), India (Punjab), Canada (Ontario), and the U.S. (New York, Michigan, Kansas, California). It is often mined then ground for use as common table salt. Large, unground crystals are sold as rock salt. Rock salt is used to melt ice, as a food preservative, and for the production of soda ash by the glass industry. | ||
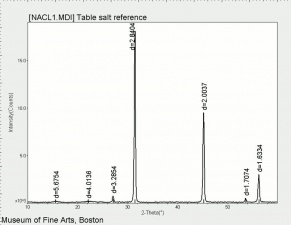
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|NACL1.jpg~XRD]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
sodium chloride; rock salt; sea salt; evaporite; halita (Esp.); halite (Port.); Halit, Steinsalz (Deut.); haliet (Ned.) | sodium chloride; rock salt; sea salt; evaporite; halita (Esp.); halite (Port.); Halit, Steinsalz (Deut.); haliet (Ned.) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Latest revision as of 13:02, 30 August 2022
Description
A mineral composed of Sodium chloride that naturally occurs as colorless, cubic crystals. Halite is found in dry lakebeds, in underground salt deposits and near the ocean. Large deposits occur in Germany, Austria, Russia, France (Dax), India (Punjab), Canada (Ontario), and the U.S. (New York, Michigan, Kansas, California). It is often mined then ground for use as common table salt. Large, unground crystals are sold as rock salt. Rock salt is used to melt ice, as a food preservative, and for the production of soda ash by the glass industry.
Synonyms and Related Terms
sodium chloride; rock salt; sea salt; evaporite; halita (Esp.); halite (Port.); Halit, Steinsalz (Deut.); haliet (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in water.
- Fluorescent.
- Salty taste.
- Transparent.
- Fracture = conchoidal.
- Streak = white.
- Luster = vitreous.
- Isometric, cubic crystals.
- Perfect cleavage in three directions with 90 degree angles.
| Composition | NaCl |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7647-14-5 |
| Mohs Hardness | 2.0 - 2.5 |
| Density | 2.4-2.6 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | 58.44 |
| Refractive Index | 1.544 |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Halite
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "halite" [Accessed December 4, 2001].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Caring for your Collections, Arthur W Schulz (ed.), Harry N. Abrams, Inc. , New York, 1992
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 8742